The ancient Egyptian pyramids have long been shrouded in mystery and fascination, captivating the minds of historians, archaeologists, and curious individuals alike. These towering structures, built thousands of years ago, stand as a testament to the ingenuity and artistic mastery of the ancient Egyptians. But beyond their impressive size and grandeur, the secrets hidden within these pyramids continue to baffle experts to this day. From the construction techniques used to the purpose they served, each pyramid holds untold stories waiting to be unraveled. In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of the ancient Egyptian pyramids, exploring their history, construction, purpose, mysteries, and the modern research that seeks to unlock their enigmatic secrets.
Contents
- The History of Egyptian Pyramids
- The Construction Techniques
- The Purpose and Function of the Pyramids
- The Pyramid Complexes
- The Pyramids’ Mysteries
- Modern Understanding and Research
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How many pyramids are there in Egypt?
- 2. Who built the Egyptian pyramids?
- 3. How were the pyramids constructed?
- 4. How long did it take to build a pyramid?
- 5. Why were pyramids built in a pyramid shape?
- 6. What treasures were found inside the pyramids?
- 7. What is the significance of the Sphinx near the pyramids?
- 8. Are there any hidden chambers in the pyramids?
- 9. What do hieroglyphs found in the pyramids reveal?
- 10. Can you go inside the pyramids?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How were the Egyptian pyramids built?
- 2. Why were the pyramids built in the shape of a pyramid?
- 3. Were the pyramids used solely as burial tombs?
- 4. How were the pyramids aligned with astronomical events?
- 5. What mysteries are still hidden within the Egyptian pyramids?
- 6. How have modern technologies helped in exploring the pyramids?
- 7. What evidence supports the theory that the pyramids were built by manual labor?
- 8. Were the pyramids only built during the Old Kingdom period?
- 9. How were the pyramids protected from tomb robbers?
- 10. What role did the Sphinx play in the pyramid complexes?
- References
- Read More
The History of Egyptian Pyramids
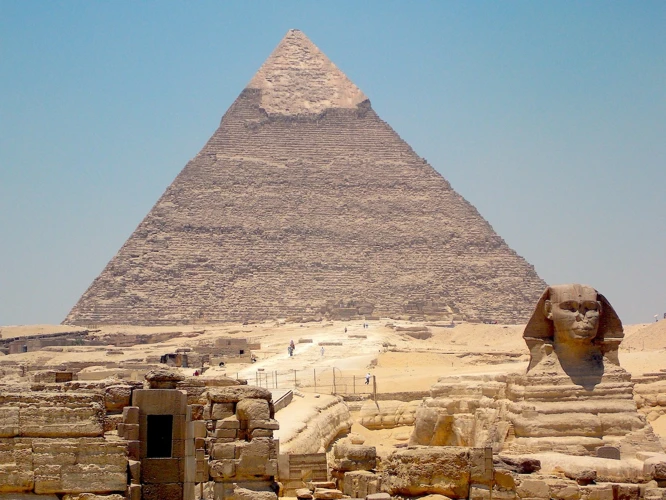

The history of Egyptian pyramids can be traced back to the Old Kingdom period of Ancient Egypt, specifically around 2686 to 2181 BCE. During this era, the construction of pyramids became a monumental undertaking, serving as royal tombs for the pharaohs. The most iconic pyramids are located in Giza, just outside of modern-day Cairo. The Great Pyramid of Khufu, also known as the Pyramid of Cheops, is the largest and oldest of the three pyramids at Giza. It was built as a final resting place for Pharaoh Khufu and stands as a remarkable architectural achievement. Its construction involved the careful placement of over two million stone blocks, some weighing up to 50 tons. The Pyramids of Khafre and Menkaure, built for Khufu’s successors, are equally impressive, displaying the evolution of pyramid design and construction techniques. These pyramids reflect the power and wealth of the pharaohs and remain enduring symbols of ancient Egyptian civilization. Other famous pyramids, such as the Step Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara, demonstrate the early experimentation with pyramid construction and the evolution of pyramid design. The remarkable history of Egyptian pyramids is a testament to the unwavering dedication and ingenuity of the ancient Egyptians, and continues to captivate the imagination of people around the world.
Check out more about the fascinating world of Egyptian pyramids in our article “The Rise of Ophiuchus in Actors of International Cinema“.
1. The Pyramids of Giza
The Pyramids of Giza, located on the outskirts of Cairo, Egypt, are undoubtedly the most famous pyramids in the world. These monumental structures were built during the Old Kingdom period of Ancient Egypt and served as tombs for the pharaohs. The Great Pyramid of Khufu, also known as the Pyramid of Cheops, is the largest and oldest of the Giza pyramids. It stands over 480 feet tall and was constructed using an estimated 2.3 million stone blocks. The precision of the construction is awe-inspiring, with the stones fitting together so tightly that not even a sheet of paper can be inserted between them. The second largest pyramid at Giza is the Pyramid of Khafre, built by the son of Khufu. It is slightly smaller but appears taller due to its higher elevation on the plateau. The Pyramid of Menkaure is the smallest of the three main pyramids but still an impressive structure. These pyramids were surrounded by mortuary temples and causeways that connected them to other structures in the complex. The Giza pyramids continue to fascinate visitors and researchers alike, providing insights into the advanced engineering skills and religious beliefs of the ancient Egyptians.
Learn more about the intriguing world of ancient pyramids in our article “Elemental Associations of Ophiuchus“.
2. Other Famous Egyptian Pyramids
2. Other Famous Egyptian Pyramids:
– The Bent Pyramid: Located in Dahshur, the Bent Pyramid stands out for its unique architectural design. Built during the reign of Pharaoh Sneferu, this pyramid initially had steep sides that were later altered to a more gradual angle, giving it a distinct bent appearance. The change in angle was likely due to structural concerns and serves as a testament to the experimental nature of pyramid construction during that time.
– The Red Pyramid: Also found in Dahshur, the Red Pyramid is another significant pyramid attributed to Pharaoh Sneferu. It is the third-largest pyramid in Egypt and showcases a distinct reddish hue, giving it its name. The Red Pyramid is considered one of the best-preserved pyramids in Egypt and is renowned for its well-built inner chambers and corridors.
– The Pyramid of Amenemhat III: Located in Hawara, this pyramid belongs to Pharaoh Amenemhat III of the 12th Dynasty. While not as grand in scale as the pyramids of Giza, it stands out for its unique architectural features. The core of the pyramid was made of mud bricks, and its outer layer was covered with limestone, giving it a distinctive appearance.
– The Pyramid Complex of Djedefre: Djedefre, the son of Khufu, constructed his pyramid in Abu Rawash. Although the pyramid itself is now in ruins, its complex includes notable structures such as a causeway leading to a mortuary temple and a large statue of Djedefre. The site offers insights into the architectural and religious practices of the time.
These pyramids, along with the famous ones at Giza, are just a glimpse into the rich history and architectural legacy of ancient Egypt. They serve as a testament to the skill and dedication of the ancient Egyptians in creating monumental structures that have stood the test of time.
Learn more about the intriguing world of pyramids and their significance in our article “Understanding the Strengths of Ophiuchus: A Deep Dive into Personality Traits“.
The Construction Techniques
The construction techniques employed by the ancient Egyptians in building the magnificent pyramids were nothing short of remarkable. These monumental structures were crafted using precise methodologies and a deep understanding of engineering principles. The primary building material used was limestone, which was abundant and readily available in the surrounding areas. The blocks of limestone were quarried and then transported to the construction site using a combination of ramps, sleds, and possibly even boats for river transport. The stones were carefully cut and shaped to fit together seamlessly, creating the smooth outer surfaces of the pyramids. The engineering prowess of the ancient Egyptians is evident in the precision with which these blocks were aligned, with an accuracy of just a few millimeters. To lift and maneuver the heavy stones, the ancient Egyptians likely utilized a combination of ramps, levers, and sledges, possibly aided by wooden rollers. The construction process required an immense amount of labor, with thousands of workers involved in each project. The techniques and tools used by the ancient Egyptians in building the pyramids showcase their architectural expertise and unparalleled craftsmanship, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to amaze us today.
1. Building Materials Used
When it comes to the construction of Egyptian pyramids, the choice of building materials played a crucial role in ensuring their durability and longevity. The primary material used for the core structure of the pyramids was limestone, which was abundant in the nearby quarries of Egypt. Limestone blocks were carefully cut and shaped to fit together tightly, creating a solid and stable foundation. The outer layer of the pyramids, known as the casing stones, was made of fine white limestone. These polished stones gave the pyramids their iconic smooth appearance, reflecting the sun’s rays and making them gleam in the desert landscape. Other materials, such as granite and basalt, were also utilized for specific architectural features and decorative elements within the pyramid complexes. The choice of these materials not only provided strength and stability but also showcased the artistic and aesthetic sensibilities of the ancient Egyptians. The use of durable and locally sourced materials ensured that the pyramids stood the test of time and became enduring symbols of architectural grandeur.
The construction of Egyptian pyramids required a wide array of tools and equipment, all of which contributed to the precision and efficiency of the builders. The ancient Egyptians utilized both manual and mechanical tools during the construction process. Some of the essential manual tools included copper chisels, wooden mallets, and dolerite balls. These chisels were used to shape and carve the stones, while the mallets provided the necessary force for their manipulation. The dolerite balls, known as pounders, were used in the quarrying process to detach the stones from the bedrock. In addition to manual tools, advanced machinery, such as pulleys and ramps, were used to transport and lift the heavy stone blocks. The construction of ramps allowed the builders to raise the stones to higher levels, while the pulleys facilitated the lifting and positioning of the stones into place. The ingenuity and skill of the ancient Egyptian builders, combined with their extensive knowledge of engineering principles, allowed them to overcome the challenges of constructing these monumental structures with remarkable precision and mastery.
2. Tools and Equipment
The construction of Egyptian pyramids required a wide array of tools and equipment, showcasing the remarkable craftsmanship of ancient Egyptian builders. The primary tool used in pyramid construction was the simple yet indispensable ramp, which allowed workers to move heavy stone blocks to higher levels. Ropes and sledges were used to transport these blocks, utilizing the power of human labor and sometimes aided by animals. The chisel was a crucial tool for shaping and carving the stones with precision, while the level ensured the accuracy of the pyramid’s alignment. To measure angles, the ancient Egyptians used the plumb bob and the gnomon, a device similar to a sundial. The shaduf, a primitive crane-like mechanism, was employed to lift heavy objects. For smoothing and polishing the surfaces of the pyramid, sandstone and limestone were rubbed against the stone blocks. These tools and equipment, though seemingly basic by modern standards, were essential to the monumental task of pyramid construction, showcasing the ingenuity and resourcefulness of the ancient Egyptians.
The Purpose and Function of the Pyramids
The Pyramids of ancient Egypt served as multifunctional structures, with their primary purpose being the final resting place for the pharaohs. These monumental tombs were carefully designed and constructed to ensure the preservation of the pharaoh’s mortal remains and their journey to the afterlife. The intricate burial chambers within the pyramids housed the pharaoh’s mummified body, along with valuable treasures and offerings that would accompany them in the afterlife. The pyramids were constructed in strategic locations, aligning with the cardinal directions and with specific astronomical orientations, emphasizing the pharaoh’s connection to the gods and the cosmos.
In addition to their role as tombs, the pyramids held great religious and spiritual significance for the ancient Egyptians. They were believed to be the meeting place between the earthly realm and the divine realm. The shape of the pyramid, with its sloping sides, was seen as a symbol of the sun’s rays descending from the heavens to touch the earth. This connection between heaven and earth was central to the ancient Egyptian concept of rebirth and the eternal cycle of life.
The pyramids also functioned as symbols of the pharaoh’s divine power and authority. Their massive size and grandeur conveyed the pharaoh’s status as a god-king, ruling over both the mortal realm and the realm of the gods. The construction of the pyramids required enormous resources, including a vast labor force and a sophisticated organizational structure. This endeavor showcased the pharaoh’s wealth and the strength of the Egyptian civilization as a whole.
The purpose and function of the pyramids encompassed both practical and symbolic elements, serving as the final resting place for the pharaohs, connecting the earthly with the divine, and embodying the power and glory of ancient Egypt.
1. Tomb of Pharaohs
The pyramids of Ancient Egypt served as the final resting places for the pharaohs, making them monumental tombs of great significance. These massive structures were constructed with the belief that they would provide a safe and eternal dwelling for the pharaoh’s soul in the afterlife. Inside the pyramids, intricate burial chambers were constructed, often containing elaborate sarcophagi where the mummified remains of the pharaohs were placed. The surrounding walls were adorned with elaborate hieroglyphic inscriptions and depictions of gods, intended to protect and guide the pharaoh’s spirit in the journey to the afterlife. The grandeur of the pyramid complex extended beyond the burial chamber, with ancillary structures such as storerooms, chapels, and offering halls providing sustenance and provisions for the pharaoh’s afterlife. The meticulous burial rituals and the extensive preparations involved in constructing these tomb-like structures highlight the immense importance Egyptians placed on ensuring the eternal well-being of their pharaohs. These tombs within the pyramids became the ultimate symbol of divine power and the pharaoh’s everlasting legacy.
2. Religious and Spiritual Significance
The Egyptian pyramids hold immense religious and spiritual significance in ancient Egyptian society. They were not only tombs for the pharaohs but also served as a connection between the earthly realm and the afterlife. The Egyptians believed in the concept of an afterlife and believed that in order for the pharaoh to continue their journey in the next world, their bodies had to be preserved. The pyramid structure, with its soaring height and majestic presence, was seen as a ladder that would help the pharaohs ascend to the realm of the gods. The pyramid’s triangular shape represented the rays of the sun god Ra, further emphasizing its divine connection. Inside the pyramids, elaborate burial rituals took place, including the placement of precious items and offerings to ensure the pharaoh’s comfort in the afterlife. The walls of the burial chambers were adorned with religious text known as the Pyramid Texts, containing spells and incantations to guide and protect the pharaoh’s soul on its eternal journey. The pyramids were not just solitary structures but were often part of a larger complex that included temples and other religious structures. These complexes were places of worship and pilgrimage, with priests performing rituals and ceremonies to honor the pharaohs and their connection with the gods. The religious and spiritual significance of the Egyptian pyramids played a central role in the ancient Egyptian belief system, demonstrating the deep reverence and devotion they had for their pharaohs and their gods.
To learn more about the intriguing world of ancient Egyptian beliefs and religion, check out our article “Elemental Associations of Ophiuchus“.
The Pyramid Complexes

The pyramid complexes surrounding the Egyptian pyramids were not just standalone structures but were part of a larger architectural ensemble. These complexes served various functions and were intricately designed to serve both practical and symbolic purposes. One key feature of these complexes is the Sphinx, a majestic statue with the body of a lion and the head of a human. The Great Sphinx of Giza, located near the Pyramid of Khafre, is the most famous and enigmatic of all sphinxes. With its massive size and mysterious smile, the Sphinx has been a source of fascination for centuries. The temples within the pyramid complexes were important religious and ceremonial spaces. These temples were dedicated to the worship of deities and were used for various rituals associated with the pharaoh’s burial and the afterlife. Another notable feature of the pyramid complexes is the Solar Boat Pit. These pits were designed to house disassembled boats which were believed to carry the pharaoh’s soul across the sky in the afterlife. The boats, meticulously constructed and adorned, were buried to accompany the pharaoh on their journey to the afterlife. The pyramid complexes in ancient Egypt were not just mere architectural elements, but they formed a complex network of structures and symbolism, reflecting the religious, spiritual, and cultural beliefs of the ancient Egyptians. These archaeological sites continue to provide valuable insights into the intriguing world of ancient Egyptian civilization.
1. Sphinx and Temples
The Sphinx and the temples surrounding the Egyptian pyramids add an extra layer of intrigue and wonder to these architectural marvels. The Sphinx, a mythical creature with the body of a lion and the head of a human (believed to represent Pharaoh Khafre), stands as a guardian at the entrance of the Giza plateau. Its colossal size and enigmatic expression have fascinated visitors for centuries. Surrounding the pyramids are various temples that were an integral part of the pyramid complexes. The Valley Temple, located near the Sphinx, was primarily used for mummification rituals and served as a connection between the mortuary temple and the pyramid. The Mortuary Temple, situated adjacent to the pyramid, played a crucial role in the funerary cult of the pharaoh, where rituals and offerings honoring their afterlife were carried out. These temples were constructed with massive stone blocks, featuring intricate carvings and hieroglyphs that provided insights into religious beliefs and rituals of ancient Egypt. The combination of the Sphinx and the temples creates a captivating landscape, further deepening the sense of awe and mystery surrounding the Egyptian pyramids.
2. Solar Boat Pit
The Solar Boat Pit is an intriguing feature found in the vicinity of some Egyptian pyramids. These pits were specially constructed to house large, elaborately designed boats known as solar boats or solar barges. The purpose of these boats was connected to the Egyptian belief in the afterlife and the journey of the pharaohs’ souls to the underworld. The boats were believed to carry the deceased pharaohs on their spiritual voyage, symbolizing their transition from the earthly realm to the divine. The Solar Boat Pit associated with the Great Pyramid of Khufu is one of the most famous examples. Discovered in 1954, the pit contained the dismantled pieces of a well-preserved, ancient boat with intricate carvings and decorative details. The boat was meticulously reconstructed and is now on display in a dedicated museum at the pyramid complex. It offers valuable insight into the ancient Egyptians’ craftsmanship and their spiritual beliefs. The Solar Boat Pit provides a fascinating glimpse into the rituals and rituals surrounding the pharaohs’ burial practices, shedding light on the cultural and religious significance of these magnificent structures.
The Pyramids’ Mysteries
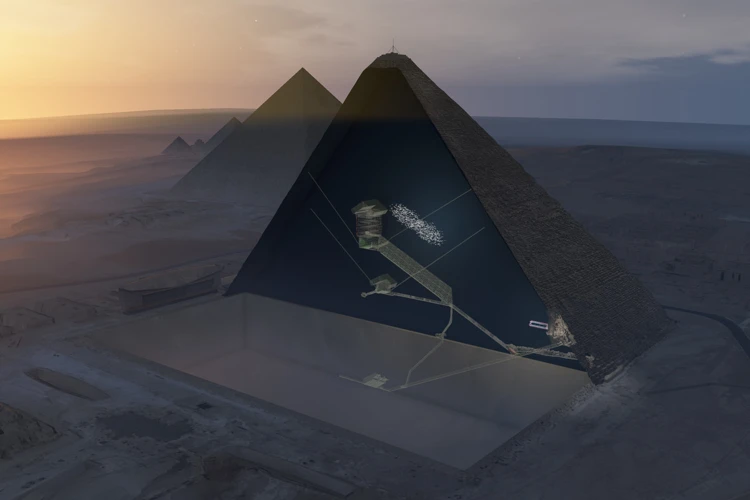

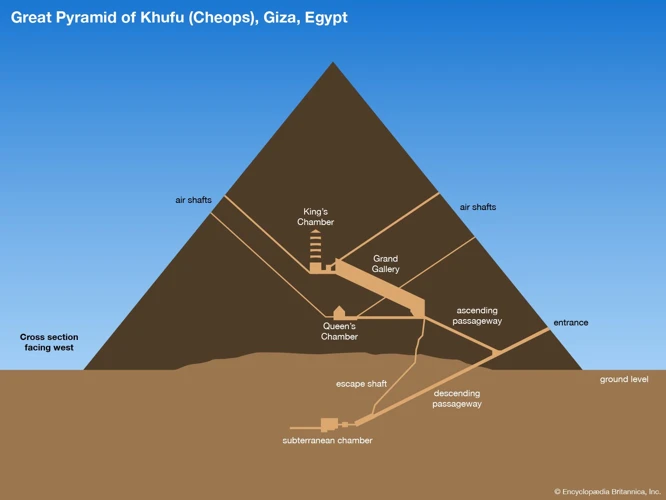
The pyramids of ancient Egypt hold a plethora of mysteries that continue to intrigue researchers and enthusiasts alike. One of the most enduring enigmas is the existence of secret chambers within the pyramids. Despite extensive exploration and study, there are still unexplored areas in many pyramids. For example, in the Great Pyramid of Khufu, a mysterious void known as the “Big Void” was discovered in 2017, sparking speculation about its purpose and contents. This chamber-like cavity, measuring about 30 meters in length, remains largely unexplored and its significance remains a mystery.
Additionally, the pyramids exhibit remarkable mathematical and astronomical significance. The alignment of the pyramids with celestial bodies, such as the stars of Orion’s Belt, has long intrigued researchers. Some theories suggest that the layout of the pyramids reflects a deliberate attempt to mimic the positioning of heavenly bodies, possibly as a means of connecting the pharaohs with the gods. The precise mathematical calculations involved in constructing pyramids with such accuracy also raise questions about the knowledge and techniques possessed by the ancient Egyptians.
The pyramid texts, inscriptions found in the burial chambers of pyramids, further add to the mysteries surrounding these structures. These ancient texts contain religious and magical spells believed to guide the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife. The decipherment and interpretation of these texts have provided valuable insights into the religious beliefs and rituals of the ancient Egyptians but have also revealed complexities that are yet to be fully understood.
While many theories and hypotheses have been proposed to explain these mysteries, their true nature and purpose continue to elude us. The pyramids stand as enigmatic symbols of an ancient civilization and their mysteries serve as a constant reminder of the wealth of knowledge that the ancient Egyptians possessed.
Look further into the secrets and mysteries of the pyramids in our article “Elemental Associations of Ophiuchus“.
1. Secret Chambers
The presence of secret chambers within the Egyptian pyramids adds an air of mystery and intrigue to these ancient structures. Over the centuries, archaeologists and explorers have discovered hidden chambers within some pyramids, revealing additional insights into their construction and purpose. One of the most famous examples is the discovery of the “King’s Chamber” within the Great Pyramid of Khufu. This chamber, located in the heart of the pyramid, is believed to have held the sarcophagus of Pharaoh Khufu. The intricate construction of the chamber, with its meticulously fitted stones and impressive granite coffer, suggests a level of craftsmanship and architectural precision beyond the initial purpose of burial. Another notable example is the “Queen’s Chamber” within the same pyramid, which features a different layout and design. The purpose of these chambers, particularly the hidden ones, remains a subject of debate and speculation among researchers. Some theories propose they may have served symbolic or religious purposes, while others suggest they were used for the preservation of sacred objects or as architectural features to distribute the weight of the pyramid. The existence of these secret chambers within the Egyptian pyramids continues to fuel curiosity and ongoing exploration, as researchers seek to uncover more of the secrets they hold.
2. Mathematical and Astronomical Significance
The Egyptian pyramids hold not only architectural and historical significance but also mathematical and astronomical importance. It is believed that the ancient Egyptians possessed advanced knowledge of mathematics and celestial observations, which they incorporated into the construction of their pyramids. One remarkable example of this is the alignment of the sides of the pyramids to the cardinal points of the compass – north, south, east, and west – with incredible accuracy. The precision of these alignments suggests a deep understanding of geometry and astronomy. Additionally, the pyramids’ internal chambers and passageways are thought to be aligned with specific celestial bodies, such as the stars of Orion’s Belt. This alignment is believed to have held significant religious and symbolic meaning for the ancient Egyptians.
The proportions and dimensions of the pyramids also exhibit mathematical precision. For instance, the ratio of each pyramid’s height to half the base perimeter, known as the pyramid’s “slope angle,” is remarkably close to the mathematical constant pi (π). This alignment with pi suggests that the ancient Egyptians were not only skilled engineers but also had a profound understanding of mathematics. The pyramid’s design and layout reflect various mathematical principles, such as the Fibonacci sequence and the golden ratio.
The inclusion of these mathematical and astronomical elements in the construction of the pyramids suggests that they served not only as grand tombs but also as cosmic monuments, representing the ancient Egyptian’s connection to the celestial realm. The intricate interplay between mathematics, astronomy, and spirituality in the design of the pyramids showcases the advanced knowledge and cultural significance held by the ancient Egyptians.
The mathematical and astronomical significance of the Egyptian pyramids highlights the sophistication and intellectual prowess of ancient Egyptian civilization. From the precise alignments to the intricate mathematical ratios, these structures stand as a monument to the profound knowledge and understanding of the natural world possessed by the ancient Egyptians. They continue to astound modern observers and inspire further exploration and study.
If you’re interested in learning more about Egyptian pyramids, be sure to read our article “Understanding the Elemental Associations of Ophiuchus“, which delves into the deeper mysteries surrounding this celestial phenomenon.
Modern Understanding and Research
Modern understanding and research have played a crucial role in unraveling the secrets of ancient Egyptian pyramids. Archaeological discoveries continue to provide valuable insights into the construction, purpose, and symbolism of these monumental structures. Excavations around pyramid complexes have unearthed artifacts, including statues, hieroglyphic texts, and burial items, shedding light on the religious beliefs and rituals associated with pyramid construction. Advancements in technology have revolutionized the study of pyramids. Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) has been used to detect hidden chambers and passages within pyramids, revealing previously unknown areas. High-resolution imaging techniques, such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), have enabled researchers to create detailed three-dimensional maps of pyramid sites, aiding in the understanding of their architectural features. The use of drones has also allowed for aerial surveys and documentation of the pyramids from unique perspectives. Additionally, scientific analysis of the materials used in pyramid construction, such as the composition of the stones and the pigments on their surfaces, provides valuable information about ancient building techniques and craftsmanship. Through these modern approaches, researchers continue to uncover new findings and refine their understanding of these ancient marvels.
1. Archaeological Discoveries
Archaeological discoveries have played a crucial role in unraveling the secrets of ancient Egyptian pyramids. Over the years, numerous excavations and studies have provided valuable insights into the construction techniques, purpose, and hidden chambers of these monumental structures. One significant discovery was made in 1922 when British archaeologist Howard Carter unearthed the tomb of the young pharaoh Tutankhamun in the Valley of the Kings. The discovery of this intact tomb revealed a wealth of artifacts and provided a glimpse into the opulence and rituals associated with royal burials. Another breakthrough came in the 1990s with the exploration of the Great Pyramid of Khufu. A French architect named Jean-Pierre Houdin proposed a theory that there might be hidden chambers within the pyramid. Using 3D imaging and non-invasive techniques, a team led by French archaeologist Franck Monnier discovered a previously unknown void above the pyramid’s Grand Gallery. This find has sparked further debate and intrigue surrounding the purpose and hidden secrets of the pyramids. These and other archaeological discoveries continue to shed light on the ancient Egyptians’ architectural mastery, their religious and cultural practices, and their understanding of the afterlife.
2. Technologies Used in Exploration
When it comes to exploring the ancient Egyptian pyramids, modern technology has played a crucial role in unraveling their mysteries. Archaeologists and researchers have utilized various advanced technologies to gain valuable insights into these ancient structures. One such technology is Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR), which uses radar pulses to create detailed underground maps. GPR has been instrumental in identifying hidden chambers and passages within the pyramids, allowing researchers to uncover new discoveries without damaging the structures. Another innovative technology used in pyramid exploration is LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging). This remote sensing method involves shooting laser pulses from aircraft to create highly accurate 3D models of the pyramids and their surrounding areas. LiDAR has been particularly useful in mapping the entire pyramid complexes, enabling researchers to study the layout and architecture in unprecedented detail. Additionally, drones equipped with high-resolution cameras have been employed to capture aerial images and footage of the pyramids from unique angles, providing a fresh perspective for analysis. These technological advancements have revolutionized the field of pyramid exploration, allowing researchers to delve deeper into the secrets of these ancient marvels while preserving their integrity.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the ancient Egyptian pyramids continue to be a source of awe and wonder, as they represent the remarkable accomplishments of a civilization that thrived thousands of years ago. These architectural marvels not only serve as tombs for the pharaohs but also carry immense religious, spiritual, and cultural significance. The construction techniques employed in building the pyramids, the intricate pyramid complexes surrounding them, and the mysterious chambers and mathematical alignments within them, all contribute to the enigma and allure that surround these structures. Modern research and archaeological discoveries have shed light on various aspects of the pyramids, but many mysteries still remain. The study of Egyptian pyramids allows us to glimpse into a past civilization, their beliefs, and their quest for immortality. As we continue to explore and unravel the secrets of ancient Egyptian pyramids, we gain a deeper understanding of our shared human history and the remarkable capabilities of ancient civilizations.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How many pyramids are there in Egypt?
Egypt is home to over 100 pyramids, with the most famous and well-preserved ones being located in Giza, near Cairo.
2. Who built the Egyptian pyramids?
The pyramids were built by the ancient Egyptians, particularly during the Old Kingdom period, as tombs for their pharaohs, who were considered divine rulers.
3. How were the pyramids constructed?
The pyramids were built using limestone blocks quarried from nearby areas. The blocks were cut, transported, and then meticulously placed in position to create the pyramid shape.
4. How long did it take to build a pyramid?
The construction of pyramids varied in duration depending on their size and complexity. The Great Pyramid of Giza, for example, is estimated to have taken around 20 years to complete.
5. Why were pyramids built in a pyramid shape?
The pyramid shape was believed to represent the Benben, a sacred stone associated with the creation of the world. It also symbolized the pharaoh’s ascent to the afterlife.
6. What treasures were found inside the pyramids?
Although many pyramids were looted over time, some treasures and artifacts have been discovered within them, including precious jewelry, statues, and funerary objects.
7. What is the significance of the Sphinx near the pyramids?
The Sphinx, a mythical creature with the body of a lion and the head of a human, is believed to guard the pyramids and protect the pharaoh’s burial place. Its purpose and meaning continue to be debated by scholars.
While some pyramids have hidden chambers and passages, not all have been fully explored. Ongoing research using advanced technologies aims to uncover any undiscovered secrets within these ancient structures.
9. What do hieroglyphs found in the pyramids reveal?
Hieroglyphs found inside the pyramids provide valuable insights into the beliefs, rituals, and daily life of ancient Egyptians, as well as the stories and accomplishments of the pharaohs.
10. Can you go inside the pyramids?
Visitors are allowed to enter certain pyramids, such as the Great Pyramid of Khufu, although access to certain areas may be restricted. It’s a unique opportunity to experience the awe-inspiring interiors of these monumental structures.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How were the Egyptian pyramids built?
The Egyptian pyramids were built using a construction technique called “corbelling,” where layers of stones were placed on top of each other in a sloping formation. The stones were cut and shaped using copper tools, and a large workforce of laborers was employed to transport and stack them into place.
2. Why were the pyramids built in the shape of a pyramid?
The pyramid shape was chosen for its symbolic significance. In Egyptian culture, the pyramid represented the sacred Benben stone, which was believed to be the first mound of land to emerge from the primeval waters. The pyramid shape was also believed to have a strong connection to the sun and the afterlife.
3. Were the pyramids used solely as burial tombs?
While the primary purpose of the pyramids was to serve as burial tombs for pharaohs and their families, they also had religious and spiritual significance. The pyramid complexes were designed as elaborate centers for ritual and worship, with temples and altars dedicated to various gods and goddesses.
4. How were the pyramids aligned with astronomical events?
The ancient Egyptians possessed advanced knowledge of astronomy and were able to align the pyramids with celestial bodies. The alignment of certain pyramids, such as the Great Pyramid of Giza, has been found to correspond to important astronomical events, such as the rising and setting of specific stars.
The Egyptian pyramids continue to hold many mysteries that have yet to be fully unraveled. Some believe that there are secret chambers and hidden passages within the pyramids, waiting to be discovered. The mathematical and astronomical significance of the pyramid’s dimensions and alignments also remains a topic of ongoing research and speculation.
6. How have modern technologies helped in exploring the pyramids?
Modern technologies, such as ground-penetrating radar and laser scanning, have been instrumental in exploring the pyramids without causing damage to the ancient structures. These technologies allow archaeologists and researchers to uncover hidden chambers, map the internal structures of the pyramids, and gain a deeper understanding of their construction and purpose.
7. What evidence supports the theory that the pyramids were built by manual labor?
Archaeological evidence, such as the discovery of worker’s villages near pyramid sites, provides strong support for the theory that the pyramids were built by manual labor. The presence of tools, such as copper chisels and wooden sleds, further reinforces this hypothesis.
8. Were the pyramids only built during the Old Kingdom period?
While the majority of the Egyptian pyramids were built during the Old Kingdom period (approximately 2686-2181 BC), pyramid construction continued into the Middle Kingdom (approximately 2055-1650 BC) and even the New Kingdom (approximately 1550-1077 BC). However, the style and purpose of the pyramids evolved over time.
9. How were the pyramids protected from tomb robbers?
The pyramids were protected by elaborate security measures to prevent tomb robbers from accessing the valuable treasures and burial goods within. These measures included hidden passageways, false doors, and complex burial chambers with intricate traps and obstacles.
10. What role did the Sphinx play in the pyramid complexes?
The Sphinx, a mythical creature with the body of a lion and the head of a human, played a significant role in the pyramid complexes. It was considered a guardian and protector of the pyramids and was often associated with the sun god Ra. The Sphinx also acted as a symbol of royal power and authority.






