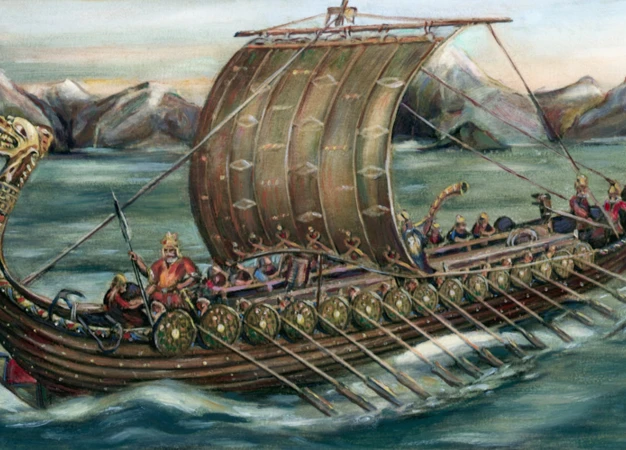
The Trailblazing Vikings: Exploring their Impact on History
From the mists of time emerges a fearless and enigmatic group that would forever leave an indelible mark on history – the Vikings. Renowned for their seafaring prowess, the Vikings forged an era known as the Viking Age, characterized by exploration, conquest, and cultural exchange. In this in-depth article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Vikings, tracing their origins, society, and cultural practices. We will journey with them as they embarked on their daring expeditions across Europe and even set foot in North America. Additionally, we will explore the profound influence that the Vikings had on trade and commerce, religious and mythological beliefs, and the enduring legacy they left behind. Join us on this captivating voyage and discover the captivating tale of the Viking trailblazers.
Contents
- The Viking Age
- Exploration and Expansion
- Impact on Trade and Commerce
- Religious and Mythological Influence
- Legacy and Influence
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Viking Age begin?
- 2. Were all Vikings fierce warriors?
- 3. What impact did Viking exploration have on Europe?
- 4. Did the Vikings really reach North America?
- 5. How did Viking trade networks operate?
- 6. What were some key beliefs in Norse mythology?
- 7. How did the Vikings influence Christianity?
- 8. What is the cultural legacy of the Vikings?
- 9. How did the Vikings shape the course of history?
- 10. Where can one find Viking artifacts and historical sites today?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- How did the Viking Age begin?
- What drove the Vikings to embark on their voyages?
- What were Viking longships like?
- Did the Vikings only raid and pillage, or did they establish settlements?
- Who were some famous Viking explorers?
- What impact did the Vikings have on trade and commerce?
- What was Norse mythology like?
- Did the Vikings have any influence on Christianity?
- What is the cultural legacy of the Vikings?
- What were the historical implications of Viking exploration?
- References
- Read More
The Viking Age
The Viking Age was a remarkable period in history that spanned from the late 8th century to the early 11th century. During this time, the Vikings, a seafaring people hailing from the Scandinavian region, embarked on a series of daring expeditions and conquests that would shape the course of history. The Vikings, known for their navigational skills and mastery of shipbuilding, expanded their reach far beyond their homeland, venturing into Europe, the Mediterranean, and even as far as North America. Their journeys not only showcased their formidable military might but also fostered cultural exchange, creating a lasting impact on the regions they encountered. The Viking Age is a testament to the audacity, resilience, and exploration of a people whose exploits continue to enthrall and captivate the imaginations of people worldwide.
1.1 Origins and Expansion
The origins and expansion of the Vikings are shrouded in mystery and intrigue. While there is no definitive answer as to where they came from, historical evidence suggests that they emerged from the Scandinavian regions of modern-day Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. The Vikings were skilled seafarers, using their advanced shipbuilding techniques to embark on voyages of exploration and conquest. Their mastery of the sea allowed them to navigate treacherous waters, reaching as far as Russia, Constantinople, and even the Middle East. Their expansion was not limited to conquering new lands, but also involved establishing vital trade routes, creating a robust network that linked distant regions together. The Viking expansion was driven by various factors, including overpopulation, limited resources, and a thirst for adventure and wealth. Their raids and conquests not only brought them fame and riches but also instilled fear in the hearts of those who stood in their way. The Viking expansion forever changed the political and cultural landscape of the regions they encountered, leaving an enduring impact that can still be felt to this day.
1.2 Viking Society and Culture
Viking society and culture were richly complex and deeply rooted in their Norse heritage. The Vikings were organized into a hierarchical structure, with the chieftain holding the highest position of authority. Society was divided into classes, with Jarls (aristocrats) at the top, followed by free farmers, merchants, and then thralls (slaves). The Norse society placed great emphasis on honor and loyalty, as depicted in their sagas and epic poetry. These works celebrated heroic deeds and showcased the importance of warfare and bravery in Viking society.
Religion played a significant role in Viking culture, with the belief in Norse mythology shaping their daily lives. Norse mythology was a pantheon of gods and goddesses, including Odin, Thor, and Freya, each representing various aspects of nature and human existence. The Vikings believed in an afterlife that included Valhalla, where fallen warriors would reside after death. These religious beliefs influenced every aspect of their lives, from the rituals performed during births and marriages to the burial customs of their deceased.
Art and craftsmanship were highly valued in Viking culture. They excelled in metalwork, creating intricate jewelry, amulets, and weaponry. Their artistic expression was also evident in their storytelling through intricate wood carvings, known as the “Urnes style,” which depicted mythological figures and stories. Additionally, poetry and oral storytelling were deeply cherished, as skalds (poets) played a crucial role in Viking society, reciting sagas and stories of heroes past.
The Vikings were avid traders, establishing far-reaching trade networks across Europe and beyond. They exchanged goods such as furs, amber, and slaves, and their voyages brought them into contact with different cultures, leading to the assimilation of various traditions and customs. This cultural exchange not only enriched Viking society but also contributed to their reputation as skilled merchants and navigators.
Viking society and culture were a tapestry of social hierarchies, religious beliefs, artistic expression, and thriving trade networks. Their values of honor, bravery, and craftsmanship defined their existence and left a lasting impact on the world. The profound influence of Viking society and culture can still be seen today in various aspects of modern Scandinavian heritage and folklore.
Exploration and Expansion
During the era of exploration and expansion, the Vikings pushed the boundaries of their known world and embarked on incredible voyages of discovery. Venturing into Europe, the Vikings launched raids, established settlements, and traded extensively. One notable figure during this time was Leif Erikson, who is believed to have reached North America around 1000 AD, several centuries before Christopher Columbus. This Norse explorer’s journey to Vinland, as documented in the sagas, showcases the Vikings’ intrepid spirit and their willingness to explore uncharted territories. The Vikings’ exploration and expansion not only left an enduring impact on the lands they reached but also influenced cultural exchange, shaping the course of history and paving the way for future explorers and adventurers. Their legacy of exploration and expansion embodies the spirit of discovery and the Viking’s unrivaled seafaring capabilities.
2.1 Viking Experiences in Europe
Viking Experiences in Europe were marked by both conquest and cultural exchange. Fierce and fearless warriors, the Vikings embarked on numerous raids and invasions throughout Europe, leaving a lasting impact on the regions they encountered. From the British Isles to the coasts of France and Iberia, their swift longships struck fear into the hearts of coastal communities. These raids were not only driven by a desire for plunder but also a thirst for adventure and exploration. However, the Vikings’ interaction with Europe was not solely characterized by violence. They also established trading posts and settlements, engaging in commerce and forging connections with local communities. These interactions created a fusion of cultures, as the Vikings borrowed ideas, technology, and even architectural styles from the lands they explored. One of the most notable Viking contributions to European culture was their influence on the Norman dynasty, which would go on to shape the history of England and beyond. The Viking experiences in Europe were a complex tapestry of conquest, trade, cultural assimilation, and influence, which continue to fascinate historians and enthusiasts to this day.
2.2 Leif Erikson and North America
Leif Erikson, a legendary Viking explorer, played a significant role in the Viking exploration of North America. According to Norse sagas, Leif Erikson set sail from Greenland and arrived in a place he called Vinland, which is believed to be present-day Newfoundland, Canada. This expedition, estimated to have occurred around the year 1000, predates Christopher Columbus’s arrival in the Americas by about 500 years.
Leif Erikson’s voyage to North America demonstrated the Vikings’ exceptional navigational skills and their ability to traverse vast distances across treacherous waters. The Norse sagas recount his encounters with indigenous peoples known as the Skrælings, suggesting that the Vikings established some form of contact or trade with the native inhabitants.
The Viking presence in North America, although short-lived and limited in terms of permanent settlements, remains a remarkable feat in exploration history. It provides evidence of the Vikings’ willingness to venture into unknown territories, leaving a mark on the New World long before other European powers.
Leif Erikson’s exploration of North America serves as a testament to the audacity and adventurous spirit of the Viking people. While their presence in North America did not lead to significant long-term colonization, it paved the way for future explorations and interactions between Europeans and the indigenous peoples of the Americas.
To learn more about other legendary figures in history, check out our article on the fascinating tale of Robin Hood, the outlaw hero, who defied authority and fought for justice in medieval England.
Impact on Trade and Commerce
The Vikings had a profound impact on trade and commerce during their reign. Through their extensive voyages and conquests, they established a vast trading network that stretched across Europe and beyond. One notable trading route was the Varangian Trade Route, which connected the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea. The Vikings, known as the Varangians in the East, utilized this route to establish lucrative trade relationships with the Byzantine Empire and other Eastern powers. They traded a variety of goods, including furs, timber, honey, and slaves, in exchange for precious metals, spices, silk, and other exotic commodities. This flourishing trade not only brought wealth to the Viking communities but also stimulated economic growth and cultural exchange between distant regions. The Viking impact on trade and commerce was not only far-reaching but also laid the foundation for the development of future trade networks and shaped the economic landscape of the medieval world.
3.1 The Trading Network of the Varangians
The Trading Network of the Varangians was a vital component of Viking trade and commerce during the medieval period. The Varangians were a group of Scandinavian traders and warriors who navigated the rivers of Eastern Europe, establishing connections with the Byzantine Empire and the vast lands of the Middle East. Known for their skilled seafaring and navigational abilities, the Varangians played a significant role in facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture between the Viking world and the Byzantine Empire. They sailed along rivers such as the Volga, Dnieper, and Don, forming a crucial trade route that connected the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea. The Varangians provided a link between the riches of the East and the Norse societies, bringing sought-after commodities such as furs, honey, and slaves from the north to the markets of Byzantium. In return, they acquired luxurious goods like silk, spices, silver, and Byzantine coinage, enriching the Viking societies. This trading network not only boosted economic prosperity but also fostered cultural and diplomatic ties between the Vikings and the Byzantines. The Varangians’ presence in the East had a lasting impact, as evidenced by the presence of Norse runestones in areas such as Ukraine and Russia, highlighting their enduring influence in these regions. The Trading Network of the Varangians stands as a testament to the Vikings’ remarkable capability to navigate distant lands and establish prosperous trade routes, fueling their status as trailblazers of the medieval world.
3.2 Viking Trade Routes
Viking trade routes were the lifeblood of their economy and played a crucial role in their expansion and cultural influence. These intrepid seafarers established extensive trade routes that stretched across the known world of their time. The Vikings navigated the treacherous waters of the North Atlantic, the Baltic Sea, and even ventured down the rivers of Eastern Europe. Their trade routes connected regions as far as Constantinople in the Byzantine Empire, the Abbasid Caliphate in the Middle East, and the Volga River in present-day Russia. The Vikings traded a variety of goods, including furs, timber, amber, and slaves. They also imported luxury items such as silk, spices, and precious metals. The trading network of the Vikings, known as the Varangians, was particularly lucrative, with major trading hubs like Novgorod and Kiev. These routes not only facilitated commerce but also paved the way for cultural exchange, as the Vikings interacted with different peoples and absorbed new ideas. The Viking trade routes were an essential component of their exploration and expansion, establishing their reputation as skilled merchants and fearless adventurers.
Religious and Mythological Influence
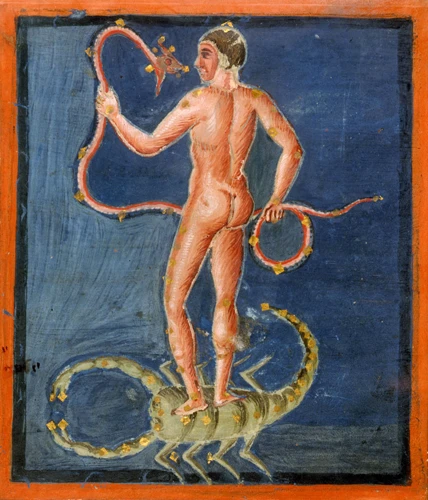

Religious and mythological beliefs held a profound influence over the Viking culture and society. The Vikings practiced a polytheistic religion known as Norse mythology, which worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses with their own unique powers and domains. The most prominent of these deities was Odin, the Allfather and ruler of Asgard, who held sway over war, wisdom, and magic. Other notable gods and goddesses included Thor, the god of thunder and protector of mankind, and Freya, the goddess of love, beauty, and fertility. These mythological beliefs influenced every aspect of Viking life, from daily rituals and festivals to their artistic expressions and even their exploration voyages. Additionally, the Viking impact on Christianity cannot be overlooked. As they came into contact with Christian communities during their expeditions, some Vikings gradually converted to Christianity, merging elements of their own belief system with the newfound faith. This religious and mythological tapestry created a rich and captivating spiritual landscape that continues to fascinate to this day.
4.1 Norse Mythology
Norse Mythology, a central aspect of Viking culture, encompasses a rich tapestry of gods, goddesses, and mythical creatures. The Norse pantheon includes powerful deities such as Odin, the Allfather and god of wisdom, Thor, the thunder god known for his strength and protection, and Loki, the mischievous trickster and shape-shifter. Each deity possesses unique characteristics and attributes, and their stories often intertwine in epic sagas and legends. The Vikings believed in a complex cosmology, with nine worlds interconnected by the World Tree, Yggdrasil. These worlds housed various beings, including giants, dwarves, and elves. The Norse mythological tradition also features vivid tales of heroic deeds and battles, with renowned figures like Sigurd, the slayer of dragons, and the Valkyries, fierce warrior maidens who selected the fallen in battle. The myths and legends of Norse Mythology provided the Vikings with a framework for understanding the world and their place within it, offering lessons in valor, honor, and the impermanence of life. This rich mythology continues to captivate and inspire people today, inspiring works of literature, art, and even popular culture like Marvel’s Thor.
4.2 The Viking Impact on Christianity
The Viking Impact on Christianity was a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. As the Vikings expanded their reach and engaged in trade and settlement across Europe, they came into contact with Christian communities. Initially, the Vikings were primarily pagans, following their own Norse mythology and religious practices. However, through their interactions with Christian societies, they began to encounter and explore Christianity. This exposure led to a gradual assimilation and integration of Christian beliefs and practices into Viking culture. The Vikings adopted certain aspects of Christianity while also infusing it with their own unique interpretations and traditions. This syncretism resulted in a distinct blend of Norse mythology and Christian theology. The convergence of these two religious systems can be seen in the art and artifacts of the Viking Age, such as the monumental crosses found in areas where the Vikings settled. These crosses often bear intricate Viking designs and symbols, showcasing the blending of Christian and Viking influences. The Vikings’ conversion to Christianity had significant political implications as well. Many Viking leaders recognized the diplomatic and economic benefits that came with aligning with Christian powers, leading to their own conversion and the subsequent Christianization of their realms. This process of assimilation and adaptation demonstrates the profound impact the Vikings had on Christianity and the lasting legacy of their religious and cultural exchange.
Legacy and Influence

The legacy and influence of the Vikings can be seen in various aspects of society and culture. One of their enduring cultural legacies is their rich mythology, which continues to captivate and inspire people around the world. Norse mythology, with its pantheon of gods and epic tales of heroism and adventure, has influenced art, literature, and even popular culture to this day. The Vikings’ impact on Christianity is also noteworthy, as their encounters with Christian communities and their eventual conversion shaped the development of religious beliefs in the regions they inhabited. Additionally, the Vikings’ intrepid exploration and navigational skills paved the way for future discoveries and trade routes, leaving a lasting impact on global commerce. From their remarkable craftsmanship to their fearless spirit of exploration, the Vikings’ legacy lives on as a testament to their trailblazing spirit and indelible mark on history.
5.1 Cultural Legacy
The cultural legacy of the Vikings is undeniably vast and far-reaching. As they explored and interacted with different regions, the Vikings left behind a lasting impact that influenced various aspects of culture. One of the most notable contributions is their language, Old Norse, which laid the foundation for modern Scandinavian languages such as Danish, Swedish, and Norwegian. The Vikings’ rich mythology and sagas, filled with gods, heroes, and epic tales, continue to fascinate and inspire creative works in literature, art, and even modern-day media. The Viking artistic style, characterized by intricate metalwork, wood carving, and shipbuilding techniques, is celebrated for its craftsmanship and beauty. The Vikings’ seafaring achievements and their skill in navigation and exploration have had a lasting impact on maritime traditions and exploration. The exploration and settlement of places like Iceland, Greenland, and even Vinland (believed to be present-day North America) demonstrate their intrepid spirit and their ability to adapt to new environments. Today, Viking festivals, museums, and historical reenactments keep their cultural legacy alive, allowing people to immerse themselves in the fascinating world of the Vikings and gain a deeper understanding of their contributions to human history.
5.2 Historical Implications
The historical implications of the Vikings are vast and enduring. Their explorations and conquests during the Viking Age left an undeniable impact on the regions and cultures they encountered. One significant historical implication of the Vikings’ actions was the establishment of trade networks and routes that connected distant lands. Through their extensive voyages, the Vikings not only expanded their own wealth and resources but also facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies between different regions. This flourishing trade network played a pivotal role in the development of interconnected economies and cultural diffusion throughout Europe and beyond.
The Viking presence and influence had a profound impact on the political landscape of Europe. The raids and conquests of the Vikings disrupted established power structures, causing political instability and reshaping the dynamics of the regions they targeted. In response to the Viking threat, many European kingdoms and territories were forced to adapt their defenses and alliances, leading to significant shifts in political strategies and diplomatic relations.
The Vikings also played a role in shaping the medieval period in Europe. Their raids and invasions contributed to a sense of insecurity and instability, which prompted the construction of fortified towns and castles as defensive measures. This increased militarization had long-lasting effects on the social, economic, and architectural aspects of medieval society.
Additionally, the Viking Age marked the beginning of sustained contact and interaction between the Norse people and Christian societies. As Vikings came into contact with Christian communities during their expeditions and through peaceful trade, they became exposed to Christianity. This exposure resulted in a gradual conversion of some Vikings to Christianity, leading to a fusion of Norse pagan beliefs with Christian practices. The influence of Viking culture and mythology can still be seen in the art, literature, and folklore of the regions they influenced.
The historical implications of the Vikings are far-reaching and multi-faceted. Their voyages, trade networks, impact on political structures, and cultural exchanges significantly shaped the development of medieval Europe and beyond. Today, the Viking legacy continues to capture the imagination and fascination of people around the world, reminding us of their enduring historical significance.
Conclusion

The Viking trailblazers have undoubtedly left an enduring legacy that continues to captivate our imaginations. Through their remarkable exploration and expansion, the Vikings not only impacted the territories they encountered but also shaped the course of history. Their navigational skills and seafaring prowess allowed them to venture far and wide, establishing trade routes, forging new settlements, and leaving a lasting mark on various cultures. The Viking Age, characterized by their audacious exploits and cultural exchange, serves as a testament to their resilience, daring spirit, and thirst for exploration. From their origins and society to their impact on trade and religion, the Vikings have left an indelible imprint on the world. Their cultural legacy still resonates across various spheres, influencing art, literature, and even popular culture.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did the Viking Age begin?
The Viking Age is believed to have begun with the infamous raid on the Lindisfarne monastery in 793 AD. This marked the first recorded Viking attack on Anglo-Saxon England and set the stage for the subsequent Viking incursions throughout Europe.
2. Were all Vikings fierce warriors?
Contrary to popular belief, not all Vikings were warriors. While pillaging and raiding did play a significant role in Viking culture, not every Viking participated in such activities. Many Vikings were farmers, traders, craftsmen, and explorers, contributing to the diverse nature of their society.
3. What impact did Viking exploration have on Europe?
Viking exploration had a profound impact on Europe. Through their expeditions, the Vikings established trade routes, established settlements, and left their mark on the cultural and linguistic landscapes of the regions they settled, such as Normandy in modern-day France and Dublin in Ireland.
4. Did the Vikings really reach North America?
Yes, the Vikings did reach North America. Led by the intrepid explorer Leif Erikson, they established a settlement known as Vinland around the year 1000 AD. This makes them the first known Europeans to have reached the continent, predating Christopher Columbus by nearly 500 years.
5. How did Viking trade networks operate?
Viking trade networks were extensive and interconnected. The Vikings traded a variety of commodities, including furs, honey, weapons, and slaves. They established trading posts and hubs, such as Hedeby in Denmark, Birka in Sweden, and Kaupang in Norway, to facilitate their trade activities.
6. What were some key beliefs in Norse mythology?
Norse mythology was rich in symbolism and mythical beings. Some key figures included Odin, the All-Father and ruler of the gods, Thor, the god of thunder and fertility, and Freyja, the goddess of love and beauty. Norse mythology also featured concepts like Valhalla, the afterlife for slain warriors.
7. How did the Vikings influence Christianity?
The Vikings’ interaction with Christianity was complex. While initially wary of the new religion, the Vikings eventually embraced Christianity and played a crucial role in its spread throughout Scandinavia and beyond. They formed alliances with Christian rulers and participated in the conversion of their societies.
8. What is the cultural legacy of the Vikings?
The cultural legacy of the Vikings can still be seen today in various aspects. Their language, Old Norse, has influenced modern Scandinavian languages. The Vikings also left an impact on art, literature, and architecture, with intricate metalwork, epic sagas, and distinctive Viking longhouses serving as enduring examples.
9. How did the Vikings shape the course of history?
The Vikings had a profound influence on the course of history. Their exploration and expansion led to cultural exchange and the establishment of trade routes that connected distant lands. They also contributed to the rise of medieval kingdoms, shaped the political landscape of Europe, and left a lasting imprint on maritime history.
10. Where can one find Viking artifacts and historical sites today?
Viking artifacts and historical sites can be found in various parts of the world. Museums such as the Viking Ship Museum in Oslo, Norway, and the National Museum of Denmark house impressive collections of Viking relics. Additionally, archaeological sites like Jelling in Denmark and the Isle of Man offer glimpses into Viking history and culture.
References
- History of the Vikings: An Enthralling… by Wellman, Billy
- Follow the Paths of Viking Raiders from Norway to North …
Frequently Asked Questions

How did the Viking Age begin?
The Viking Age began with the first recorded Viking raid on the British Isles in 793 AD. This marked the start of a period of extensive exploration and expansion by the Norse seafarers.
What drove the Vikings to embark on their voyages?
The Vikings were driven by a combination of factors, including a desire for wealth and treasure, a search for new trading routes, as well as a thirst for adventure and glory.
What were Viking longships like?
Viking longships were long and narrow vessels, designed for both sailing and rowing. They had a shallow draft, which allowed them to navigate through shallow waters and rivers.
Did the Vikings only raid and pillage, or did they establish settlements?
While the Vikings were known for their raids and plundering, they also established settlements in areas such as Iceland, Greenland, and parts of England. These settlements were often used as trading posts and bases for further exploration.
Who were some famous Viking explorers?
Some famous Viking explorers include Leif Erikson, who is believed to have reached North America centuries before Columbus, and Erik the Red, who founded the first Norse settlements in Greenland.
What impact did the Vikings have on trade and commerce?
The Vikings played a crucial role in the development of trade networks across Europe. They established trade routes, such as the trading network of the Varangians, and facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between different regions.
What was Norse mythology like?
Norse mythology was a complex belief system that included gods like Odin, Thor, and Loki. It encompassed a rich tapestry of myths, legends, and epic tales that shaped Viking culture and influenced their worldview.
Did the Vikings have any influence on Christianity?
Yes, the Vikings had a significant influence on Christianity. As they came into contact with Christian societies through their explorations, they adopted and adapted certain Christian practices and beliefs into their own religious traditions.
What is the cultural legacy of the Vikings?
The cultural legacy of the Vikings can be seen in various aspects of modern society, including language, literature, art, and even sports. Many words in English, for example, have their roots in Old Norse, the language of the Vikings.
What were the historical implications of Viking exploration?
The Viking exploration and expansion had far-reaching historical implications. It contributed to the spread of Norse culture, the exchange of knowledge and ideas across Europe, and even influenced the course of world history through their voyages to North America.






