Before the invention of writing systems as we know them today, ancient civilizations found innovative ways to tell stories, capture history, and convey information. One such civilization was ancient Egypt, renowned for its rich culture and mesmerizing art. Among their many artistic achievements, the ancient Egyptians developed a unique system of writing, known as hieroglyphics, which served as a captivating medium for storytelling. The use of intricate symbols and pictorial representations allowed the ancient Egyptians to communicate complex narratives, myths, and legends through their hieroglyphic texts. In this article, we will delve into the art of storytelling through ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics, exploring their evolution, decoding techniques, and the preservation of their rich narratives.
Contents
- Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics: An Overview
- The Evolution of Hieroglyphics as a Storytelling Medium
- Tools and Techniques for Decoding Hieroglyphics
- Unraveling Ancient Egyptian Myths and Legends
- Symbolism and Visual Narratives in Hieroglyphic Art
- Preservation and Interpretation of Hieroglyphic Storytelling
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How were hieroglyphics created?
- 2. How did hieroglyphics evolve as a storytelling medium?
- 3. What was the purpose of hieroglyphics?
- 4. How were hieroglyphic symbols and their meanings deciphered?
- 5. What is the significance of the Rosetta Stone in understanding hieroglyphics?
- 6. How did ancient Egyptians structure their stories using hieroglyphics?
- 7. Can hieroglyphics tell us about ancient Egyptian myths and legends?
- 8. What are some famous ancient Egyptian myths and legends depicted in hieroglyphics?
- 9. How did ancient Egyptians use symbolism in their hieroglyphic art?
- 10. How do modern Egyptologists contribute to the understanding of hieroglyphics?
- References
- Read More
Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics: An Overview
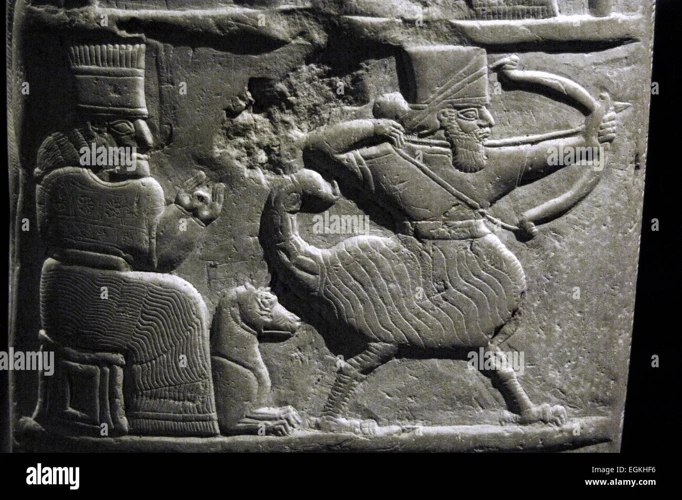

Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics were an intricate system of writing that played a crucial role in the civilization’s culture and communication. Hieroglyphics, which means “sacred carvings” in Greek, were primarily used in religious, governmental, and funerary contexts. They were inscribed on temple walls, tomb paintings, papyri, and various artifacts. The writing system featured a combination of phonograms, logograms, and ideograms, allowing for a complex and nuanced means of expression. In this overview, we will explore the origins and purpose of hieroglyphics, the development of hieroglyphic writing, and the symbolism behind the hieroglyphic symbols and their meanings.
Hieroglyphics originated around 3,400 BCE and were influenced by earlier Egyptian writing systems. They were initially used for practical purposes, such as recording business transactions and keeping economical records. However, over time, hieroglyphics evolved into a medium for storytelling, mythology, and religious beliefs. The usage of hieroglyphics expanded, making it a vital part of the ancient Egyptian civilization’s cultural and artistic expression.
Hieroglyphics consist of a vast and diverse collection of symbols that represent a wide range of concepts, objects, and ideas. These symbols include depictions of animals, plants, objects, and human figures, each possessing its own distinct meaning. Some symbols are phonetic, representing specific sounds, while others are ideographic, representing entire words or concepts. The combination of these symbols allowed for a complex and flexible writing system.
In the next sections, we will explore the tools and techniques used to decode hieroglyphics, the unraveling of ancient Egyptian myths and legends through hieroglyphics, as well as the symbolism and visual narratives displayed in hieroglyphic art. So let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this ancient form of storytelling!
The Evolution of Hieroglyphics as a Storytelling Medium

The ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics underwent a fascinating evolution as a storytelling medium. From their practical origins as a means of record-keeping, hieroglyphics gradually transformed into a complex and expressive form of narrative communication. This evolution can be attributed to several key factors, including advancements in writing techniques, the development of standardized scripts, and the deep cultural and religious significance associated with hieroglyphics.
The Origins and Purpose of Hieroglyphics
The origins of hieroglyphics can be traced back to the Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt, around 3,400 BCE. Initially, hieroglyphics were utilized for administrative purposes, such as recording inventories and regulating trade. However, with the rise of a centralized government and an increasingly complex society, the usage of hieroglyphics expanded to encompass more than just practical matters.
The Development of Hieroglyphic Writing
As ancient Egyptian society progressed, so did the sophistication of their hieroglyphic writing system. The early hieroglyphics consisted of simple pictorial representations of objects and concepts. Over time, these pictorial signs evolved into more abstract symbols, allowing for a greater range of meanings and concepts to be conveyed.
Hieroglyphic Symbols and Their Meanings
Hieroglyphics boasted a diverse collection of symbols, with each symbol representing a particular sound, word, or idea. These symbols encompassed a wide range of subjects, from human and animal figures to celestial bodies and natural elements. The artists who created hieroglyphics used a combination of phonograms (symbols representing sounds) and ideograms (symbols representing whole words or concepts) to construct their narratives.
The Transformation of Hieroglyphics into a Storytelling Medium
As the ancient Egyptians delved further into mythology, religion, and historical events, hieroglyphics became an essential medium for storytelling. Carved on temple walls or depicted in tomb paintings, hieroglyphics captured mythological tales, divine legends, and historical events. These narratives allowed the ancient Egyptians to pass down stories of their gods, heroes, and ancestors through generations.
This evolution of hieroglyphics as a storytelling medium intertwined with the religious and cultural practices of ancient Egyptian society. The hieroglyphic inscriptions not only conveyed stories but also served as a means of honoring the gods, celebrating kingship, and preserving the legacy of the deceased.
In the next sections, we will explore the tools and techniques used to decode hieroglyphics, the unraveling of ancient Egyptian myths and legends through hieroglyphics, as well as the symbolism and visual narratives displayed in hieroglyphic art. So, let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this ancient form of storytelling!
The Origins and Purpose of Hieroglyphics
The origins of hieroglyphics can be traced back to ancient Egypt around 3,400 BCE. The ancient Egyptians developed this intricate system of writing as a means to communicate and preserve their knowledge, beliefs, and history. Initially, hieroglyphics were primarily used for practical purposes such as keeping records of trade and economic transactions. However, they soon evolved into a much broader form of communication, encompassing religious, governmental, and artistic domains.
One of the primary purposes of hieroglyphics was to document the religious beliefs and rituals of the ancient Egyptians. They believed that writing was a sacred act, and hieroglyphics were considered a direct gift from the gods. The hieroglyphic texts found in temples and tombs often depicted scenes of worship, offerings, and the interactions between mortals and deities. These writings provided a means for the Egyptians to connect with their gods, honor their ancestors, and ensure an afterlife.
Hieroglyphics also served as a medium for recording historical events, including the achievements of pharaohs and important military campaigns. The ancient Egyptians used hieroglyphics to celebrate triumphs, establish royal lineages, and emphasize the divine nature of their rulers. The inscriptions on monuments and obelisks immortalized the exploits of pharaohs, depicting their victorious battles and benevolent rule.
Hieroglyphics played a vital role in the preservation and transmission of knowledge. They were used to record scientific observations, architectural plans, astronomical measurements, and medical remedies. Hieroglyphic texts found in papyri and manuscripts provided a valuable resource for future generations to understand the innovations and discoveries of the ancient Egyptians.
In addition to their practical uses, hieroglyphics held symbolic significance. The intricate symbols and representations conveyed deeper meanings beyond their literal interpretations. The ancient Egyptians believed that words, when written in hieroglyphics, possessed magical qualities and had the power to manifest reality. Hieroglyphic inscriptions were seen as a way to invoke the gods and access divine wisdom.
The purpose of hieroglyphics, therefore, encompassed both practical and spiritual aspects of ancient Egyptian life. It allowed for the preservation of history and knowledge, the expression of religious beliefs, and the affirmation of pharaonic power. The complexity and beauty of hieroglyphics continue to captivate and inspire awe to this day, providing a unique insight into the ancient Egyptian civilization and their rich cultural heritage.
The Development of Hieroglyphic Writing
The development of hieroglyphic writing in ancient Egypt was a gradual process that spanned thousands of years. It evolved from earlier primitive forms of communication, such as pictographs and ideographs, into a sophisticated system capable of conveying complex ideas and narratives.
1. Pictographic Roots: The earliest form of hieroglyphic writing consisted of simple pictographs, which were recognizable representations of objects or concepts. These pictographs were used to convey basic information and were often carved or painted onto stone or pottery.
2. Ideographic Expansion: As Egyptian society became more complex, the need for a more extensive writing system arose. Hieroglyphics began to incorporate ideograms, which represented ideas or abstract concepts rather than specific objects. This expansion allowed for a more versatile and nuanced means of expression.
3. Phonograms and Determinatives: To further enhance the flexibility of the writing system, hieroglyphics eventually incorporated phonograms and determinatives. Phonograms represented specific sounds or syllables, while determinatives were symbols placed at the end of a word to provide additional context or clarify meaning.
4. Hieratic and Demotic Scripts: As hieroglyphics became more widespread, two simplified script forms emerged: hieratic and demotic. Hieratic script was a cursive form of hieroglyphics used for everyday writing purposes, while demotic script was even more simplified and was used for administrative and legal documents.
5. Decline and Reinterpretation: With the advent of the Ptolemaic period, hieroglyphic writing gradually fell out of common usage and was replaced by the Greek alphabet. For many centuries, hieroglyphics remained a mysterious and undecipherable script. It wasn’t until the discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799 that scholars were able to unlock the secrets of this ancient writing system.
The development of hieroglyphic writing in ancient Egypt demonstrates the remarkable ingenuity and adaptability of this civilization. Through the evolution of pictographs, ideograms, phonograms, and determinatives, the ancient Egyptians created a complex and expressive writing system that served as a cornerstone of their culture and storytelling traditions. It is through the decipherment and interpretation of hieroglyphics that we are able to unravel the mysteries of this ancient civilization and gain insights into their rich history and mythology.
Hieroglyphic Symbols and Their Meanings
Hieroglyphic symbols were the building blocks of the ancient Egyptian writing system, each with its own distinct meaning and significance. These symbols allowed the ancient Egyptians to convey a wide range of concepts, ideas, and objects through their hieroglyphic texts. Let’s explore some of the most common hieroglyphic symbols and their meanings:
1. Phonetic Symbols: These hieroglyphs represented specific sounds or syllables. For example, the symbol of a reed leaf (𓇋) represented the sound “au” while the symbol of an owl (𓆏) represented the sound “m.”
2. Determinative Symbols: These hieroglyphs helped clarify the meaning of a word by acting as classifiers. They provided context to the written text. For instance, the symbol of a human figure (𓃀) placed after a word indicated that the word pertained to a person.
3. Ideographic Symbols: These hieroglyphs represented entire words or ideas. A prime example is the symbol of an eye (𓁹) which represented the word “seeing” or “knowledge.”
4. Semantic Complements: These symbols were used to indicate the general meaning or sense of a word. For example, the symbol of a mouth (𓉐) was commonly added to words associated with speaking or singing.
It is important to note that hieroglyphics could also be combined to create compound words or convey more complex concepts. The interpretation of hieroglyphic symbols often required an understanding of the context in which they were used, as well as the phonetic and visual elements of the language.
The study of hieroglyphic symbols and their meanings has been greatly aided by the discovery of the Rosetta Stone, which provided a key breakthrough in understanding ancient Egyptian writing. This ancient artifact featured the same decree inscribed in three scripts: hieroglyphics, demotic script, and Greek. Comparing the Greek text, which was already known, with the hieroglyphic text allowed scholars to decipher the meanings of many hieroglyphic symbols.
By studying the symbols and deciphering their meanings, researchers and Egyptologists have strived to unlock the secrets of ancient Egyptian culture, history, and mythology. The symbolism embedded in hieroglyphic texts has provided invaluable insights into the beliefs, practices, and daily life of this remarkable civilization.
Tools and Techniques for Decoding Hieroglyphics

Decoding hieroglyphics was a challenging task that required the use of specific tools and techniques. One of the most significant breakthroughs in understanding hieroglyphics came with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799 by Napoleon’s troops during their campaign in Egypt. The Rosetta Stone, a stele with inscriptions in three different scripts – hieroglyphics, Demotic script, and Greek – provided a crucial key to decoding hieroglyphics. The Greek text on the stone served as a translation guide, enabling scholars to decipher the meanings of the hieroglyphic symbols.
Deciphering hieroglyphics also required the study and analysis of the grammar and structure of the ancient Egyptian language. Scholars examined the patterns and repetitions within the hieroglyphic texts to identify common words and phrases. They developed theories on the grammar rules and syntax of the language, which aided in translating and understanding the hieroglyphic narratives. This process involved comparing multiple texts and building a comprehensive understanding of the language’s rules and conventions.
Another important aspect of decoding hieroglyphics was the contextual interpretation of the symbols. Hieroglyphic symbols often had multiple meanings depending on their context within a sentence or a narrative. For example, a symbol that represented the god Osiris might have a different meaning when used in a religious context compared to a historical account or a mythological story.
Over time, the decipherment of hieroglyphics led to the creation of dictionaries and grammar guides, assisting scholars in their pursuit of understanding the ancient Egyptian language. Today, advancements in technology, such as digital imaging and computational linguistics, have further aided in the decoding process by enabling more precise analysis and comparison of hieroglyphic texts.
The tools and techniques used for decoding hieroglyphics have not only provided insights into the ancient Egyptian civilization but have also expanded our understanding of linguistics and the development of writing systems. The Rosetta Stone, along with the perseverance and dedication of Egyptologists and linguists, has unlocked the secrets of this mesmerizing form of storytelling, allowing us to delve into the myths, legends, and history of ancient Egypt.
The Rosetta Stone: A Breakthrough in Understanding Hieroglyphics
The Rosetta Stone played a pivotal role in deciphering the ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics, leading to a breakthrough in understanding this intricate writing system. Discovered in 1799 in the Egyptian town of Rosetta, the stone is a black basalt slab inscribed with a decree issued in 196 BCE during the reign of Ptolemy V. What made the Rosetta Stone extraordinary was that it contained the same text in three different scripts: hieroglyphics, demotic (a simplified script used for everyday purposes), and Greek. This provided a key to unlocking the meaning of hieroglyphics by allowing scholars to compare the known translation of the Greek text with the unknown hieroglyphic script.
The Rosetta Stone sparked further understanding and study of hieroglyphics, and it became the foundation for deciphering the ancient Egyptian writing system. One of the key figures in this endeavor was Jean-François Champollion, a French linguist and scholar. By meticulously studying the hieroglyphics on the stone and making connections with the Greek text, Champollion was able to decipher the phonetic values of many hieroglyphic symbols. His groundbreaking work laid the foundation for understanding the grammar, structure, and vocabulary of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics.
Thanks to the Rosetta Stone’s inscriptions, historians and linguists were finally able to unlock the secrets of the once-mysterious hieroglyphics. It marked a significant turning point in our ability to access and comprehend the stories, myths, and cultural aspects encoded within these ancient texts. The Rosetta Stone serves as a reminder of the importance of ancient artifacts and their role in unraveling the mysteries of the past.
In the next section, we will explore the process of deciphering the grammar and structure of ancient Egyptian stories, further deepening our understanding of the art of storytelling through hieroglyphics.
Deciphering the Grammar and Structure of Ancient Egyptian Stories
Deciphering the grammar and structure of ancient Egyptian stories is a fascinating and challenging task that allows us to gain a deeper understanding of the narratives conveyed through hieroglyphics. The study of grammar and structure helps us unravel the complexities of the ancient Egyptian language and how it was used to construct compelling stories.
One key aspect of deciphering ancient Egyptian stories is understanding the grammar. The Egyptian language had elements of both syntactic and inflectional grammar. Syntactic grammar refers to the arrangement of words within a sentence, while inflectional grammar deals with the inflection and modification of words to indicate tense, gender, and other grammatical features. By studying the patterns and rules governing these grammar systems, scholars have been able to piece together the structure of sentences and paragraphs in hieroglyphic texts.
Another aspect of deciphering ancient Egyptian stories is identifying the narrative structure. Stories in hieroglyphics often followed a specific pattern, with an introduction, a development of events, and a conclusion. These narratives could range from historical accounts to mythical tales, each with its distinct structure and themes.
Contextual clues and the placement of certain hieroglyphic symbols within the text also play a crucial role in understanding the grammar and structure of ancient Egyptian stories. For example, determinative symbols were used to clarify the meaning of a word and to provide context.
By carefully analyzing the grammar, structure, and contextual cues within hieroglyphic texts, scholars and Egyptologists have made significant progress in decoding and interpreting the ancient Egyptian stories. Through their efforts, we have gained insight into the beliefs, values, and cultural aspects of this fascinating civilization.
In the next sections, we will unravel specific ancient Egyptian myths and legends, such as “The Adventures of Osiris” and “The Story of Isis and Horus,” exploring the depths of their narratives and the symbolism embedded within. Stay tuned for a captivating journey through the world of ancient Egyptian storytelling!
Unraveling Ancient Egyptian Myths and Legends
Unraveling ancient Egyptian myths and legends through hieroglyphics provides us with a fascinating insight into the beliefs and stories of this ancient civilization. Hieroglyphic texts have played a significant role in shedding light on the mythology and religious practices of the Egyptians. The stories depicted in hieroglyphics often revolve around their gods, heroic figures, and the concept of the afterlife.
One of the most well-known myths depicted in hieroglyphics is the story of Osiris, the god of the afterlife and the underworld. According to the myth, Osiris was betrayed and murdered by his brother Seth, who coveted his power. The hieroglyphic inscriptions on temple walls and papyri have allowed us to piece together this intricate tale of betrayal, death, and resurrection. The story also emphasizes themes of justice and the cyclical nature of life.
Another captivating myth often depicted in hieroglyphics is the story of Isis and Horus. Isis, the goddess of magic and wisdom, is depicted as a devoted mother who protects her son Horus, the rightful heir to the throne. This myth showcases the power of a mother’s love and the divine right of kingship. Through the hieroglyphic inscriptions, we gain insight into the symbolism and rituals associated with the story, as well as the religious significance attributed to these deities.
Hieroglyphic texts have provided a wealth of information on the ancient Egyptian cosmology, their pantheon of gods, and the rituals associated with their religious practices. The meticulous study and deciphering of hieroglyphics by modern Egyptologists have allowed us to unravel the narrative threads of these ancient myths and legends. By examining the symbols, the sequencing of events, and the accompanying artwork, researchers have been able to construct a more comprehensive understanding of the intertwining stories and beliefs that shaped the ancient Egyptian civilization.
As we continue to decode and interpret hieroglyphic texts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the artistry and narrative sophistication of ancient Egyptian storytelling. These stories, immortalized in hieroglyphics, not only entertained and educated the people of ancient Egypt but also provided them with a shared cultural identity and a connection to their divine beings. The study of hieroglyphics and the exploration of their mythological tales open a window into the ancient world, allowing us to marvel at the enduring power of these narratives throughout the ages.
The Adventures of Osiris: A Tale of Betrayal and Resurrection
The Adventures of Osiris is a captivating ancient Egyptian myth that is intricately woven within the hieroglyphic texts. This powerful tale revolves around Osiris, the god of the afterlife and the underworld, and his treacherous brother Set. According to the myth, Osiris was a wise and just ruler who brought prosperity and civilization to Egypt. However, Set grew jealous of Osiris’ power and plotted to overthrow him.
Set devised a plan to trick and ultimately betray Osiris. He hosted a grand feast and presented a beautifully crafted chest as a gift to whomever could fit inside it perfectly. Osiris, unaware of Set’s malicious intentions, volunteered to try. As soon as Osiris entered the chest, Set sealed it shut, trapping and drowning him in the Nile River.
Upon discovering his brother’s betrayal, Set scattered the dismembered body parts of Osiris across Egypt. Osiris’ wife, Isis, mourning the loss of her beloved husband, embarked on a journey to gather the scattered body parts in an attempt to resurrect Osiris. With the aid of her sister, Nephthys, and the god of wisdom, Thoth, Isis was able to reconstruct Osiris’ body.
Through her ancient Egyptian magical spells and the power of her love for Osiris, Isis breathed life back into him. Osiris, now resurrected, became the ruler of the afterlife and the judge of the dead. This myth exemplifies themes of betrayal, resurrection, divine justice, and the triumph of good over evil.
The story of Osiris and his resurrection is depicted in various forms of ancient Egyptian art, including elaborate temple reliefs, funerary texts, and tomb paintings. The hieroglyphic inscriptions beautifully capture the dramatic events and emotions of the myth, making it one of the most prominent narratives in ancient Egyptian storytelling.
The Adventures of Osiris not only provided ancient Egyptians with entertainment but also served as a moral compass and a representation of their religious beliefs regarding life, death, and the afterlife. This myth has intrigued scholars and Egyptologists, who have dedicated their efforts to decoding and understanding the intricate details and symbolism embedded within the hieroglyphic texts.
To dive deeper into the significance of Osiris and his story, we can examine the symbolism and meaning behind each hieroglyphic representation within the myth. From the depiction of the chest to the symbols of resurrection and divine kingship, every element of the story tells a deeper narrative. By unraveling the hieroglyphic symbols within this myth, we gain further insight into the ancient Egyptian culture, beliefs, and their profound art of storytelling.
The Story of Isis and Horus: A Mother’s Love and Divine Kingship
The story of Isis and Horus is one of the most iconic and beloved tales portrayed through ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics. It revolves around the powerful goddess Isis, known as the mother of all pharaohs and the embodiment of maternal love, and her son Horus, the falcon-headed god who would become the rightful heir to the Egyptian throne. This captivating story highlights the themes of love, sacrifice, and the divine nature of kingship.
The narrative begins with the death of Osiris, Isis’ husband and the rightful king of Egypt. Osiris was murdered by his jealous brother Seth, who desired the throne for himself. In her grief, Isis embarks on a quest to resurrect her husband and restore order to the land. Through her magical powers and unwavering determination, Isis successfully revives Osiris, although he becomes the god of the underworld, ruling over the afterlife.
Isis and Osiris conceive Horus, who represents the rightful claimant to the throne as the son of Osiris. However, Seth, knowing the threat Horus posed to his own rule, seeks to challenge his claim. The story follows a series of epic battles between Horus and Seth, each vying for the divine kingship of Egypt.
Throughout the tale, Isis plays a central role as a loving and protective mother. She fiercely defends and supports Horus, using her intelligence, cunning, and magical abilities to aid him in his battles against Seth. Together, they overcome numerous challenges and obstacles, with Isis acting as a symbol of maternal love and guidance.
The story of Isis and Horus showcases the profound role of women in ancient Egyptian society and highlights the importance of maternal love and protection. It also serves as a reminder of the continuous struggle for power and the divine rights of kingship, reinforcing the belief that the pharaohs were divinely ordained to rule.
Hieroglyphics, with their intricate symbols and visual narratives, vividly depict the different scenes and episodes of the story. Carved on temple walls and inscribed on papyri, these hieroglyphic texts bring the story to life, ensuring its immortalization for generations to come. Through the art of storytelling in hieroglyphics, the ancient Egyptians were able to convey not only historical events but also the deeper layers of human emotions and values.
Symbolism and Visual Narratives in Hieroglyphic Art

Symbolism and visual narratives play a significant role in hieroglyphic art, providing a captivating and intricate means of storytelling in ancient Egyptian culture. The use of symbols allowed the ancient Egyptians to convey deep meanings and complex narratives visually. One prominent form of hieroglyphic art can be found in the iconic tomb paintings that adorned the burial chambers of the pharaohs and nobles.
In these elaborate tomb paintings, hieroglyphic symbols were intricately incorporated, often depicting scenes from the afterlife, religious rituals, and the journey of the deceased into the realm of the gods. The use of color, perspective, and composition further enhanced the visual storytelling aspect, making the scenes come to life. Each symbol portrayed in the artwork held a specific meaning, contributing to the overall narrative and conveying the significance of various elements in the Egyptian belief system.
Temple walls also served as a canvas for hieroglyphic art, with inscriptions and carvings depicting stories of gods, pharaohs, and religious rituals. These inscriptions showcased the divine nature of the pharaoh, their connection to the gods, and the importance of religious worship in ancient Egyptian society. The hieroglyphic symbols on temple walls were not only meant to convey stories but also to invoke the protective powers of the gods and ensure the prosperity and continuity of the kingdom.
The symbolism in hieroglyphic art extended beyond individual symbols or scenes. Hieroglyphic compositions often employed symbolism through spatial arrangement and the interaction of figures. The placement of symbols in relation to one another conveyed relationships, hierarchies, and narratives. For example, the positioning of a pharaoh in a hieroglyphic scene would indicate their authority and divine status, while the depiction of gods or mythical creatures alongside particular symbols would represent their associations and roles in the story.
The use of symbolism and visual narratives in hieroglyphic art allowed the ancient Egyptians to communicate complex ideas, historical events, and religious beliefs in a visually compelling manner. These intricate artworks offer us a window into the rich cultural and mythological tapestry of ancient Egypt, providing insight into their worldview and the stories that were deemed important to pass down through generations.
In the next section, we will explore the preservation and interpretation of hieroglyphic storytelling in ancient texts and manuscripts, as well as the role of modern Egyptologists in decoding and studying hieroglyphics. So let’s continue our journey to uncover the secrets of this fascinating ancient writing system and the narratives it preserves.
The Iconic Tomb Paintings of Ancient Egypt
The tomb paintings of ancient Egypt hold a special place in our understanding of hieroglyphic storytelling. These iconic artworks, found within the burial chambers of pharaohs and elite individuals, provide a vivid glimpse into the lives and beliefs of the ancient Egyptians. The intricate and colorful scenes depicted within the tombs serve as a visual narrative, capturing important aspects of the deceased’s journey to the afterlife.
One of the most famous examples of tomb paintings is found in the tomb of Tutankhamun, commonly known as King Tut. The walls of his burial chamber depict various scenes, including the pharaoh’s funeral procession, offerings to the gods, and the judgment of the deceased in the afterlife. These elaborate paintings not only showcase the artistic skill of ancient Egyptian artisans but also convey important religious and mythological themes.
The hieroglyphic inscriptions accompanying the tomb paintings further enhance the storytelling aspect. These inscriptions provide additional context and information about the depicted scenes, identifying the individuals, gods, and rituals portrayed. Hieroglyphics were often used in conjunction with the artwork to ensure a complete understanding of the narrative being conveyed.
The tomb paintings offer valuable insights into ancient Egyptian cosmology, religious beliefs, societal structures, and daily life. They portray scenes of agricultural activities, domestic scenes, and religious ceremonies, providing a comprehensive snapshot of the ancient Egyptian civilization. Through their vibrant colors and intricate details, the tomb paintings create a visually captivating story that transcends time.
Today, these tomb paintings are not only admired for their artistic merit but also studied by Egyptologists to unravel the ancient stories and symbolism hidden within them. By deciphering the hieroglyphics and analyzing the visual elements, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the complex narratives woven into these ancient artworks.
As we explore the fascinating world of hieroglyphic storytelling, we will also delve into the role of modern Egyptologists in the preservation and interpretation of ancient Egyptian narratives. Stay tuned to discover more about the remarkable art of storytelling through hieroglyphics!
The Hieroglyphic Inscriptions on Temple Walls
The hieroglyphic inscriptions found on temple walls in ancient Egypt offer a fascinating glimpse into the rich culture and religious beliefs of the civilization. These inscriptions, meticulously carved and painted, served as important sources of information and propaganda for the ruling pharaohs and priesthood. The intricate details and deliberate placement of hieroglyphic symbols on the walls conveyed a carefully constructed narrative, showcasing the divine power and legitimacy of the pharaoh.
The inscriptions often depicted scenes of religious rituals, offerings to the gods, and important mythological events. One prominent example is the famous temple of Karnak in Thebes, which boasts extensive hieroglyphic inscriptions that span an impressive timeline of Egypt’s history. The temple walls bore the names and achievements of pharaohs, their victories in battle, and their religious interactions with the gods.
The hieroglyphic inscriptions also played a key role in legitimizing the pharaoh’s divine right to rule. The hieroglyphs often depicted the pharaoh’s interaction with deities, such as the god Amun, symbolizing the pharaoh’s close connection to the divine realm. These inscriptions reinforced the pharaoh’s status as the intermediary between the gods and the people and solidified their authority.
Additionally, the temple walls adorned with hieroglyphic inscriptions served as educational tools, conveying important religious and moral teachings to the general population. The inscriptions narrated stories of creation, emphasized the importance of ma’at (harmony and order), and instructed individuals on the proper rituals and offerings to maintain cosmic balance. The precise placement and arrangement of hieroglyphics ensured that the messages were visually striking and easily comprehensible to those who could read them.
Deciphering the hieroglyphic inscriptions on temple walls required a deep understanding of the symbolism and grammar of ancient Egyptian writing. Today, Egyptologists meticulously study and analyze these inscriptions to gain insights into the religious practices, mythologies, and historical events of ancient Egypt. The hieroglyphic inscriptions on temple walls are not just mere decorations; they are windows into the past, offering us a glimpse into the captivating world of the Egyptian civilization.
As we continue our exploration of hieroglyphic storytelling, we will delve into the preservation and interpretation of hieroglyphic texts, the role of modern Egyptologists in decoding these ancient narratives, and the tools used to unlock hidden stories and meanings. So let’s unravel the secrets of hieroglyphics and uncover the ancient tales that lie within their intricate symbols!
Preservation and Interpretation of Hieroglyphic Storytelling

Preserving and interpreting hieroglyphic storytelling is a challenging yet crucial task in understanding the ancient Egyptian culture and its narrative traditions. Over the centuries, various methods and tools have been employed to unlock the mysteries contained within hieroglyphic texts and artwork. One of the most significant breakthroughs in deciphering hieroglyphics came with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799. This ancient artifact, inscribed with a decree issued during the reign of King Ptolemy V in three scripts, including hieroglyphics, served as a key to understanding the previously indecipherable writing system.
The Rosetta Stone provided scholars with a starting point for deciphering hieroglyphics by comparing the known Greek text with the Egyptian scripts. This breakthrough allowed the meanings of many hieroglyphic symbols to be determined, leading to a deeper understanding of ancient Egyptian texts and their storytelling capabilities.
Another important aspect of interpreting hieroglyphic storytelling lies in deciphering the grammar and structure of ancient Egyptian language. Linguists and Egyptologists meticulously analyzed the hieroglyphic texts, identifying patterns in syntax and grammar to piece together the narrative flow of ancient Egyptian stories. This process involved decoding the hieroglyphic signs and determining their phonetic values, allowing for the proper pronunciation of words and the reading of texts.
The preservation of hieroglyphic storytelling is also dependent on the availability and examination of ancient texts and manuscripts. The discovery of well-preserved papyri, such as the Book of the Dead, has provided invaluable insights into the religious beliefs and funerary practices of ancient Egyptians. These texts, adorned with hieroglyphic inscriptions, offer a glimpse into the stories and myths believed by the ancient Egyptians and how they viewed life, death, and the afterlife.
Modern Egyptologists play a vital role in the continued interpretation and preservation of hieroglyphic storytelling. Through their extensive study and expertise, they delve into the complexities of ancient Egyptian culture, language, and symbolism. They meticulously analyze hieroglyphic texts, translate inscriptions, and contribute to our understanding of the stories, myths, and legends embedded in hieroglyphic art.
The preservation and interpretation of hieroglyphic storytelling require meticulous study, the use of tools like the Rosetta Stone, and a deep understanding of ancient Egyptian language and culture. Through these efforts, we can unlock the rich narratives, myths, and legends that have shaped our understanding of ancient Egypt and its captivating storytelling tradition.
Ancient texts and manuscripts hold a wealth of knowledge and stories waiting to be unlocked. In the case of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics, these texts provide invaluable insights into the narratives and beliefs of this fascinating civilization. Through the study of these ancient writings, Egyptologists have been able to piece together the stories, myths, and historical events of ancient Egypt.
One of the most famous examples of an ancient Egyptian text is the Book of the Dead, a collection of spells and rituals intended to guide the deceased through the afterlife. This funerary text was written on papyrus scrolls and often placed in tombs alongside the deceased. The Book of the Dead includes mythological narratives, instructions for navigating the underworld, and prayers for protection and safe passage.
Another important ancient text is the Pyramid Texts, a collection of spells carved into the walls of pharaoh’s pyramids during the Old Kingdom. These texts were thought to guide the deceased pharaoh on their journey to join the gods and ascend to eternal life. The Pyramid Texts contain hymns, incantations, and ritual instructions associated with the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife.
Deciphering these ancient texts and manuscripts is a painstaking process that requires a deep understanding of the hieroglyphic writing system, grammar, and vocabulary. Egyptologists combine their knowledge of the hieroglyphic symbols and grammar with archaeological evidence and comparative studies to translate and interpret these texts. This intricate work has allowed scholars to gain insights into the religious beliefs, social structure, and everyday life of ancient Egyptians.
The study of ancient texts and manuscripts not only helps us understand the narratives and stories of ancient Egypt but also sheds light on their mythology, religious practices, and societal norms. By unlocking the hidden narratives within these texts, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the art of storytelling through hieroglyphics and glimpse into the rich tapestry of ancient Egyptian culture.
Stay tuned for the next section, where we will explore the role of modern Egyptologists in decoding and studying hieroglyphics, uncovering more fascinating aspects of this ancient form of storytelling!
The Role of Modern Egyptologists in Decoding and Studying Hieroglyphics
Modern Egyptologists play a crucial role in decoding and studying hieroglyphics, allowing us to gain a deeper understanding of ancient Egyptian culture and history. Through their expertise and dedication, these scholars have made significant advancements in deciphering the complex hieroglyphic writing system.
1. Deciphering Hieroglyphics: Egyptologists employ a variety of methods and techniques to decode hieroglyphics, including the study of grammar, syntax, and comparative analysis of different texts. The Rosetta Stone, a key breakthrough in understanding hieroglyphics, provided a crucial starting point in decipherment. This ancient artifact, discovered in 1799, contains a decree written in three scripts – hieroglyphic, demotic, and Greek. By comparing the Greek text with the hieroglyphic inscriptions, scholars were able to decipher some of the symbols and establish a foundation for further decipherment.
2. Knowledge of Ancient Egyptian Language: Egyptologists dedicate years to studying the ancient Egyptian language, including its grammar, vocabulary, and syntax. This knowledge is essential in unraveling the meaning behind hieroglyphic texts, as it allows scholars to identify phonograms, determinatives, and word order. By understanding the linguistic elements of ancient Egyptian, modern Egyptologists can interpret hieroglyphs with more accuracy.
3. Multidisciplinary Approach: Egyptology is a multidisciplinary field, combining various areas of study, including archaeology, history, art history, linguistics, and anthropology. Modern Egyptologists collaborate with specialists in these fields to gain a comprehensive understanding of hieroglyphics. By analyzing the cultural context, archaeological findings, and artistic representations alongside hieroglyphic inscriptions, scholars can piece together a more complete narrative and interpretation of ancient Egyptian stories.
4. Technological Advancements: With the advancement of technology, modern Egyptologists have new tools at their disposal to aid in their research. Digital imaging techniques, such as Reflectance Transformation Imaging (RTI), allow for enhanced visualization of hieroglyphics on various surfaces. This technology helps reveal faded or damaged inscriptions, making it easier to decipher and analyze the texts.
The contributions of modern Egyptologists are invaluable in unlocking the secrets hidden within hieroglyphics. Through their meticulous work and expertise, they continue to expand our knowledge of ancient Egyptian civilization and bring the captivating stories and narratives depicted in hieroglyphic texts to life.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the art of storytelling through ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics is a testament to the creativity and ingenuity of this ancient civilization. Hieroglyphics served as a captivating medium for communication, allowing the ancient Egyptians to convey complex narratives, myths, and legends. Through their intricate symbols and pictorial representations, hieroglyphics provided a visual and textual tapestry that brought stories to life.
The overview of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics highlighted their origins, purpose, and development, showcasing the evolution of this writing system as a means of storytelling. Additionally, the tools and techniques used to decode hieroglyphics, such as the Rosetta Stone, played a vital role in unraveling the mysteries of this ancient script.
The exploration of ancient Egyptian myths and legends through hieroglyphics revealed the rich narratives of gods and goddesses, heroic adventures, and tales of love and betrayal. These stories, such as the adventures of Osiris and the story of Isis and Horus, continue to captivate and inspire us today.
The symbolism and visual narratives in hieroglyphic art not only told stories but also provided insights into ancient Egyptian beliefs, values, and societal structures. The iconic tomb paintings and hieroglyphic inscriptions on temple walls served as windows into the lives of ancient Egyptians, offering glimpses of their rituals, traditions, and aspirations.
The preservation and interpretation of hieroglyphic storytelling are ongoing endeavors, made possible through ancient texts, manuscripts, and the dedicated work of modern Egyptologists. By unlocking hidden narratives and deciphering the intricate grammar and structure of hieroglyphics, scholars continue to shed light on the rich tapestry of ancient Egyptian culture.
In the modern world, the study of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics continues to fascinate and educate people about their remarkable civilization. By understanding the ancient art of storytelling through hieroglyphics, we gain insight into the history, mythology, and cultural legacy of the ancient Egyptians.
So, next time you gaze upon the intricate symbols and hieroglyphic inscriptions of ancient Egypt, remember that they represent not only a form of writing but also a visual representation of the captivating stories that once captivated their civilization.
For more information on unlocking hidden narratives and understanding the deep symbolism of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics, you can explore the strengths and weaknesses of Ophiuchus individuals, who played an important role in deciphering and studying these ancient texts.
Frequently Asked Questions

FAQs about Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics
1. What does the word “hieroglyphics” mean?
The word “hieroglyphics” comes from the Greek words “hieros” meaning “sacred” and “glyphein” meaning “to carve.” It refers to the sacred carvings and inscriptions found in ancient Egyptian writing.
2. How old are hieroglyphics?
Hieroglyphics date back to around 3,400 BCE during the Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt. They continued to be used for several millennia, with the last known hieroglyphic inscription dating to the 4th century CE.
3. What materials were used to write hieroglyphics?
Ancient Egyptians used various materials to write hieroglyphics, including papyrus, stone, wood, ceramics, and even organic materials like ostrich eggshells. They used reed brushes or pens to apply ink made from a mixture of carbon, water, and gum.
4. How were hieroglyphics deciphered?
The breakthrough in deciphering hieroglyphics came with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799. This stone inscription contained the same text written in three scripts: hieroglyphics, Demotic script, and Greek. By comparing the languages, scholars were able to decipher the hieroglyphic script.
5. Were all ancient Egyptians able to write hieroglyphics?
No, literacy in hieroglyphics was limited to a small portion of the population, mainly scribes, priests, and members of the elite. Writing hieroglyphics required years of education and training.
6. What were the purposes of hieroglyphics?
Hieroglyphics served various purposes, including recording religious rituals and prayers, documenting historical events, recording administrative information, and as a form of artistic expression.
7. Can hieroglyphics be read like a book or a linear text?
No, hieroglyphic texts are read in different directions, depending on where the figures or glyphs are facing. They can be read left to right, right to left, or top to bottom.
8. Were there different styles or periods of hieroglyphics?
Yes, over time, the style and appearance of hieroglyphics changed. Different periods in ancient Egyptian history, such as the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom, are associated with distinct forms of hieroglyphics.
9. Were there any hieroglyphic dictionaries?
No comprehensive hieroglyphic dictionary exists. However, scholars have created lists of hieroglyphic signs and their meanings based on the extensive corpus of ancient Egyptian texts.
10. Can anyone learn to read hieroglyphics today?
Yes, with dedication and study, anyone can learn to read hieroglyphics. There are books, online resources, and courses available for those interested in exploring the fascinating world of ancient Egyptian writing.
References
- Scribes Of Ancient Egypt: The Art Of Egyptian Hieroglyphs …
- Ancient Egypt’s colourful story-telling legacy
- Hieroglyphs: unlocking ancient Egypt
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How were hieroglyphics created?
Hieroglyphics were created by ancient Egyptians using a combination of pictorial symbols and phonetic signs. The symbols were often drawn on papyrus or carved into stone.
2. How did hieroglyphics evolve as a storytelling medium?
Over time, hieroglyphics evolved from simple pictorial symbols into a more sophisticated writing system that could convey complex narratives. This allowed ancient Egyptians to tell stories in a visually engaging and symbolic way.
3. What was the purpose of hieroglyphics?
Hieroglyphics served various purposes in ancient Egypt. They were used to record historical events, document religious beliefs, and communicate important messages. They were also a way for the ancient Egyptians to express their artistic and creative abilities.
4. How were hieroglyphic symbols and their meanings deciphered?
Hieroglyphic symbols and their meanings were initially deciphered by modern scholars through the discovery of the Rosetta Stone. This artifact provided a key to understanding the hieroglyphic script by providing a parallel text in ancient Greek.
5. What is the significance of the Rosetta Stone in understanding hieroglyphics?
The Rosetta Stone played a crucial role in decoding hieroglyphics because it provided a translation of the ancient Egyptian text into a known language (Greek). This enabled scholars to begin deciphering the symbols and understanding their meanings.
6. How did ancient Egyptians structure their stories using hieroglyphics?
Ancient Egyptians structured their stories using hieroglyphics by creating sequences of symbols that represented different events or ideas. These symbols were arranged in a linear fashion to create a narrative flow and convey a specific message to the reader or viewer.
7. Can hieroglyphics tell us about ancient Egyptian myths and legends?
Absolutely! Hieroglyphics are a valuable source of information about ancient Egyptian myths and legends. Many of these stories have been preserved in hieroglyphic inscriptions on temple walls and in ancient texts and manuscripts.
8. What are some famous ancient Egyptian myths and legends depicted in hieroglyphics?
Two well-known ancient Egyptian myths depicted in hieroglyphics are “The Adventures of Osiris,” which tells the story of betrayal and resurrection, and “The Story of Isis and Horus,” which explores the themes of motherly love and divine kingship.
9. How did ancient Egyptians use symbolism in their hieroglyphic art?
Ancient Egyptians used symbolism in their hieroglyphic art to convey deeper meanings and ideas. Each hieroglyphic symbol had both a literal and symbolic meaning, allowing the artists to communicate complex concepts through visual representation.
10. How do modern Egyptologists contribute to the understanding of hieroglyphics?
Modern Egyptologists play a crucial role in deciphering and studying hieroglyphics. They use advanced techniques, such as digital imaging and detailed analysis, to further unravel the secrets of hieroglyphic storytelling and provide new insights into ancient Egyptian culture and history.
References
- Learn how to read Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphs with Ilona …
- Are Egyptian hieroglyphics considered to be writing or art, …
- Hieroglyphs: unlocking ancient Egypt






