In the enchanting realm of folklore, there exists a vast array of mythical creatures, each shrouded in mystery and imbued with symbolism that captivates the human imagination. From majestic unicorns to powerful dragons, from resurrecting phoenixes to enchanting mermaids, these mystical beings have woven their way into the tapestry of human mythology, influencing cultures and sparking our curiosity throughout the ages. Delving into the depths of these fantastical creatures, we uncover not only their unique characteristics and symbolism but also their prevalence and significance across various cultures. Join us on a journey as we explore the captivating world of mythical creatures and the symbolism they hold in folklore!
Contents
- Unicorn
- Dragon
- Phoenix
- Siren
- Centaur
- Mermaid
- Griffin
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the origin of the unicorn myth?
- Are unicorns real?
- What is the symbolism behind the unicorn’s horn?
- Do unicorns only appear in Western folklore?
- What is the significance of the unicorn in heraldry?
- Are there any famous literary works featuring unicorns?
- Do unicorns have any connections to astrology?
- Are there any real animals that resemble unicorns?
- Can unicorns fly?
- What is the significance of the unicorn in modern culture?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the origin of the unicorn myth?
- 2. What does the unicorn symbolize in folklore?
- 3. Are there any real-life animals similar to the unicorn?
- 4. What are some cultural variations of the unicorn?
- 5. What is the significance of dragons in mythology?
- 6. What do dragons symbolize in different cultures?
- 7. Are there any notable stories involving dragons in different mythologies?
- 8. What is the significance of the phoenix in folklore?
- 9. How is the symbol of the phoenix used in various cultures?
- 10. Are there any other mythical creatures similar to sirens?
- References
- Read More
Unicorn

The enigmatic unicorn, with its single spiraling horn, has long captured the fascination of humanity throughout history. This legendary creature, often associated with purity and grace, is a symbol of strength and majesty. In various folklore and mythologies, the unicorn has been depicted as a mystical being that possesses healing powers and the ability to bring good fortune to those who are worthy. It is believed to embody the virtues of courage, purity, and freedom. From ancient Greek mythology to medieval European folklore, the unicorn has left its mark on cultures across the world, becoming a symbol of hope, magic, and the untamed beauty of the natural world. Whether as a physical entity or a metaphorical representation, the unicorn continues to captivate our imagination and spark our sense of wonder and awe.
The Enigmatic Unicorn
The enigmatic unicorn, often portrayed as a horse-like creature with a single spiraling horn protruding from its forehead, has captivated the human imagination for centuries. Its elusive nature and mystical appearance have given rise to countless stories, myths, and legends. The unicorn is often associated with qualities such as purity, grace, and untamed beauty. In many tales, it is said that only the purest of hearts can catch a glimpse of this majestic creature. The horn of the unicorn, known as the alicorn, holds great significance and is believed to possess magical properties. It is said to have the power to heal ailments and neutralize poisons. This mythical creature has managed to transcend cultural boundaries, appearing in the folklore of various civilizations throughout history. From ancient Greek and Roman mythology, where it was believed to be a fierce and untamable beast, to medieval European folklore where it represented purity and chivalry, the unicorn continues to be a symbol of wonder and enchantment. Even today, the unicorn remains a popular icon in modern culture, adorning everything from clothing to home decor, as a reminder of the enduring allure of the mythical realm. (Source: [symbolic-meaning-snakes-mythology])
Symbolism of the Unicorn
The symbolism of the unicorn is rich and diverse, resonating across cultures and time. One of the prominent themes associated with the unicorn is purity. Its white coat and graceful demeanor have made it a symbol of innocence and chastity. In many tales, the unicorn is said to be able to detect both purity and impurity in individuals. This purity symbolism often extends to notions of spiritual enlightenment and transcendence. The unicorn is seen as a creature of purity and divine connection, serving as a bridge between the mortal and the divine.
Another significant aspect of unicorn symbolism is that of power and strength. Despite its gentle appearance, the unicorn is believed to possess immense strength and unwavering courage. Its single horn, often depicted as a symbol of authority and dominance, represents the creature’s untamed power. Legends often describe the horn as having magical properties, capable of healing wounds and purifying water.
The unicorn is also associated with rarity and uniqueness. Its solitary nature and elusive presence make it a symbol of individuality and the pursuit of one’s own path. This aspect of unicorn symbolism encourages individuals to embrace their own uniqueness and walk their own journey, even if it diverges from the mainstream.
The unicorn has been linked to the concept of freedom. In many myths and stories, the unicorn is depicted as a creature that cannot be tamed or captured. It embodies the spirit of freedom, encouraging individuals to break free from societal constraints and embrace their own true selves.
The symbolism of the unicorn encompasses purity, power, uniqueness, and freedom. Its mythical nature and timeless allure continue to captivate our imagination and remind us of the profound symbolism that can be found within the realm of folklore and mythology. (internal link: symbolic meaning of snakes in mythology)
Unicorn in Different Cultures
The unicorn, with its mystical allure, has found its place in the folklore and mythologies of different cultures across the globe. In Chinese culture, the unicorn, known as Qilin, is associated with prosperity and good fortune. It is often depicted with the body of a deer, the tail of an ox, and the hooves of a horse. In ancient Persia, the unicorn was believed to be a powerful creature capable of healing and purifying water. It was seen as a symbol of purity and was highly revered. In Norse mythology, a creature called the “heidrun” was believed to have the ability to produce mead from its udders. This magical creature with goat-like features shares similarities to the unicorn and serves as a potent symbol of abundance and nourishment. Additionally, in Korean folklore, the Kirin is a creature similar to the unicorn that is thought to bring good fortune and protect against evil spirits. These examples demonstrate the universal appeal and enduring presence of the unicorn in various cultures, each contributing a unique interpretation and symbolism to this enchanting creature.
Dragon

The powerful dragon, with its imposing presence and fiery breath, has been a prominent figure in mythology and folklore across the globe. Often portrayed as fearsome creatures, dragons symbolize strength, wisdom, and elemental power. In various cultures, dragons are believed to guard and protect treasures, possess knowledge, or even control natural forces. From the majestic dragons of Chinese mythology to the fire-breathing beasts of European folklore, these mythical creatures have captivated the human imagination for centuries. They embody both chaos and benevolence, representing the duality of nature and the ever-present struggle between good and evil. The symbolism and interpretation of dragons differ across cultures, but their significance is universal – they embody the awe-inspiring forces of nature and ignite our sense of wonder and fascination.
The Powerful Dragon
The Powerful Dragon, a creature of immense strength and mythical proportions, has been a prominent figure in folklore and mythology from around the world. With its serpent-like body, sharp claws, and mighty wings, the dragon is often portrayed as a formidable force to be reckoned with. In many cultures, the dragon symbolizes power, wisdom, and protection. It is often associated with the elements of fire and water, representing both destruction and creation. Dragons have been featured in various mythologies, such as the Chinese dragon, which is believed to bring good luck and prosperity, and the European dragon, which is often depicted as a fearsome creature guarding treasures. These magnificent beings have a prominent presence in popular culture, appearing in books, movies, and art, captivating the imaginations of people of all ages.
In Chinese culture, the dragon is seen as a divine creature, a symbol of imperial power. It is associated with the emperor and represents authority, strength, and good fortune. The dragon is a central figure in Chinese New Year celebrations, where dragon dances and dragon-shaped lanterns are common sights.
In European mythology, dragons are often portrayed as ferocious beasts, breathing fire and terrorizing villages. They are commonly featured in tales of knights and their quests to vanquish these mighty creatures. The heroic act of slaying a dragon is considered a symbol of bravery and triumph over evil.
Dragons also hold significance in astrology, with the recent addition of the Ophiuchus sign, which represents a serpent holder or a dragon. This addition has stirred discussions and debates among astrologers and enthusiasts alike, adding to the already fascinating lore of dragons. Whether seen as a fearsome adversary or a revered guardian, the dragon’s power and presence in folklore continue to ignite our imagination and fascination with these legendary creatures.
Symbolism of the Dragon
Known for its immense power and awe-inspiring presence, the dragon holds deep symbolism in various cultures and mythologies. Often depicted as a fearsome creature with scales and fire-breathing abilities, the dragon is associated with strength, protection, and wisdom. Its ability to fly and inhabit both land and water symbolizes harmony and balance between different elements. In many Eastern cultures, the dragon is seen as a bringer of good fortune and prosperity, representing imperial power and divine protection. In contrast, Western traditions often portray dragons as fierce adversaries, embodying chaos and the need for heroism. Despite these differences, dragons universally captivate our imagination, representing primal forces, transformation, and the eternal struggle between good and evil. The symbolism of the dragon transcends time and borders, leaving an indelible mark on art, literature, and popular culture. It continues to inspire and serve as a reminder of the immense power and potential within each of us.
Dragons in Mythology around the World
Dragons, formidable creatures revered for their immense power and mythical allure, have left an indelible mark on mythologies around the world. In Chinese mythology, the dragon is a revered creature associated with imperial power, wisdom, and good fortune. Often depicted as benevolent beings, Chinese dragons symbolize prosperity and protection. In contrast, Western mythology portrays dragons as fearsome and malevolent creatures, guarding treasures and terrorizing villages. Norse mythology presents dragons as serpentine beasts with wings and venomous breath, embodying chaos and destruction. In Indian mythology, dragons, known as Nāgas, are depicted as divine and supernatural beings with the ability to shape-shift. These variations in dragon mythology reflect the diverse cultural interpretations of this majestic creature. While the specific characteristics and symbolism may differ, dragons universally epitomize power and awe-inspiring strength. It is fascinating to explore the different mythologies and discover how dragons have captivated the imaginations of people worldwide, transcending boundaries and becoming iconic figures in folklore and popular culture.
Phoenix
The resurrecting phoenix is a mythical creature that has enthralled cultures across the globe with its tale of rebirth and rejuvenation. This majestic bird is said to have the ability to burst into flames and then rise from its own ashes, symbolizing eternal life and renewal. In various folklore and mythology, the phoenix is revered as a symbol of strength, resilience, and immortality. Its fiery plumage and regal presence have made it an enduring symbol of power and transformation. From ancient Egyptian mythology to Chinese folklore, the phoenix has left an indelible mark, often associated with the sun, creation, and the cycles of life. The symbolism of the phoenix resonates deeply within us, reminding us that even in the face of destruction, there is always the opportunity for rebirth and growth.
The Resurrecting Phoenix
The phoenix, a magnificent creature of myth and legend, is known for its ability to rise from the ashes and be reborn. This concept of resurrection has made the phoenix a symbol of immortality, renewal, and transformation. In many mythologies and folklore, the phoenix is portrayed as a majestic bird with vibrant plumage, often in shades of red, orange, and gold, representing the fiery nature of its rebirth. According to ancient Greek mythology, the phoenix has a lifespan of approximately 500 years, after which it builds a nest and sets itself on fire, only to be born anew from the ashes. This cyclical pattern of death and rebirth signifies the perpetual cycle of life, death, and renewal.
The symbolism of the phoenix expands beyond its ability to rise from the ashes. It represents resilience, strength, and the triumph of the spirit over adversity. The phoenix’s ability to overcome destruction and emerge stronger than ever serves as a beacon of hope and inspiration for those facing challenges or seeking personal transformation. In many cultures, the phoenix also embodies the concept of time and the eternal cycle of nature, connecting it to ideas of regeneration and the ever-changing cycles of life.
The phoenix is not limited to a specific culture or mythology. It has appeared in various forms across different civilizations, including ancient Egyptian, Chinese, and Native American folklore. In Egyptian mythology, the phoenix is associated with the sun god Ra and is believed to be a symbol of the daily sunrise. In Chinese mythology, the phoenix is known as the Fenghuang and represents virtue, harmony, and prosperity. Native American legends often depict the thunderbird as a phoenix-like creature, representing the power of storms and the cycle of life and death.
The allure of the phoenix lies in its ability to capture the human imagination and evoke a sense of wonder and awe. Its symbolism transcends cultural boundaries and continues to inspire individuals to overcome challenges, embrace change, and believe in the transformative power of rebirth. The phoenix reminds us that even in the face of destruction, there is always the potential for renewal and the opportunity for growth.
Symbolism of the Phoenix
Symbolism of the Phoenix:
The symbolism of the phoenix is rich and profound, representing themes of rebirth, resilience, and transformation. As a mythical bird known for its ability to rise from its own ashes, the phoenix is a powerful symbol of renewal and immortality. The fiery nature of the phoenix signifies its association with the element of fire, which represents passion, creativity, and purification. This celestial creature is often seen as a representation of hope and the promise of a new beginning, as its death and subsequent rebirth symbolize the cyclical nature of life. In many cultures, the phoenix is also associated with the sun, embodying the concept of life and light. Its ability to regenerate and emerge stronger after facing destruction represents the human capacity to overcome adversity and rise above challenges. The phoenix’s symbolism transcends cultures and time, inspiring individuals to embrace change, find strength within themselves, and embrace the transformative power of rebirth.
Phoenix in Various Folklore
The phoenix, a magnificent bird that resurrects from its own ashes, holds a prominent place in various folklore and mythologies around the world. In ancient Egyptian mythology, the phoenix was known as the Bennu bird, a symbol of the sun god Ra and associated with creation and rebirth. The Greeks also embraced the concept of the phoenix, believing it to be a symbol of immortality and renewal. According to Greek mythology, the phoenix would live for hundreds of years before building a nest of aromatic woods and setting itself ablaze. From the ashes, a new phoenix would emerge, representing the cycle of life and rejuvenation.
In Chinese folklore, the phoenix is known as the Feng Huang, often seen as the feminine counterpart to the dragon. The Feng Huang symbolizes virtue, grace, and the union of yin and yang, representing harmony and the balance of cosmic forces. It is believed to bring peace and prosperity wherever it appears.
The phoenix is also found in Middle Eastern mythology, specifically in Persian culture, where it is known as the Simurgh. The Simurgh is a benevolent, wise creature often depicted as a hybrid of bird and lion. It is associated with protection, healing, and guidance, believed to possess immense knowledge and supernatural abilities.
In each of these distinct cultures, the phoenix represents themes of resilience, transformation, and the cyclical nature of existence. Whether it’s the concept of rebirth, immortality, or harmony, the phoenix serves as a powerful symbol of hope and renewal that transcends geographical boundaries and connects humanity through a shared appreciation for the mystical and the miraculous.
Siren

The alluring siren, often depicted as half-human and half-bird, has long been a captivating figure in folklore. With their mesmerizing voices and enchanting songs, sirens were believed to lure sailors to their doom, causing shipwrecks and leading unsuspecting travelers astray. Symbolizing both temptation and danger, sirens embody the power of seduction and the depths of the human desire for both beauty and peril. In different cultures, sirens took on various forms, from mermaid-like creatures in Greek mythology to bird-like beings in ancient Near Eastern lore. Their seductive allure and haunting presence remind us of the delicate balance between desire and caution, beckoning us to explore the depths of our own desires while remaining vigilant of their potential consequences.
The Alluring Siren
The alluring siren, a captivating creature of folklore, has long held a mysterious allure over the psyche of humanity. In mythologies around the world, sirens are often depicted as beautiful seductresses with enchanting voices, luring unsuspecting sailors to their watery demise. These bewitching beings are known for their mesmerizing singing that can wrap listeners in a trance, leading them to abandon all reason and follow the irresistible call of the sirens’ melodies. In Greek mythology, sirens are said to have the upper body of a woman and the lower body of a bird, symbolizing their connection to both the land and the sea. They embody the duality of danger and temptation, representing the ever-present allure of the unknown. The symbolism of the siren extends beyond a mere cautionary tale; it serves as a metaphor for the enticing and often perilous temptations that may lead individuals astray. The siren’s bewitching song lingers throughout history as a reminder of the power of allure and the importance of exercising caution in the face of seduction.
Symbolism of the Siren
The symbolism of the Siren is deeply rooted in its alluring and seductive nature. Sirens are often portrayed as seductive and enchanting creatures, known for their captivating beauty and mesmerizing voices. They possess the power to lure sailors and travelers with their enchanting songs, leading them to their untimely demise. The Siren’s captivating allure represents temptation and the dangers of succumbing to desires that may lead to destruction. In mythology, the Siren often serves as a symbol of the irresistible allure of the unknown and the transient nature of pleasure. This symbolism serves as a cautionary tale, reminding us to resist the siren call of temptation and to exercise caution when faced with enticing distractions. The Siren’s symbolism can also be interpreted as a representation of the power of persuasion and the ability to manipulate others through charm and allure. Just like the mythical Sirens, individuals who possess this ability can captivate and persuade others through their charm and charisma. The symbolism of the Siren is a reminder to be aware of the seductive powers that may entice us and to exercise caution when making choices that may lead us astray.
Sirens in Different Cultures
In the realm of mythology, the concept of Sirens has appeared in various cultures, albeit with slight variations in their characteristics and roles. In Greek mythology, Sirens were depicted as seductive female creatures with the upper body of a woman and the lower body of a bird. They possessed enchanting voices that lured sailors towards treacherous rocks and shipwrecked them. The ancient Greeks believed that the Sirens resided on three small islands in the Mediterranean Sea.
In Norse mythology, a similar creature known as the “sjaelvarger” existed. These were mermaid-like beings who possessed the ability to foretell the future and were often associated with harbingers of danger and death. Unlike the Greek Sirens, the Norse sjaelvarger were said to have a more ominous and malevolent nature.
In Slavic folklore, the Sirens were known as “Rusalka” and were believed to be the spirits of drowned maidens. They were often depicted as beautiful, yet vengeful beings who haunted rivers and lakes, luring unsuspecting individuals to their watery demise.
The concept of Sirens can also be found in the folklore of other cultures. In ancient Mesopotamian mythology, there were creatures called “Ekimmu” who were believed to be the souls of the dead. They would roam the earth at night, looking for victims to possess and bring misfortune.
While the characteristics and roles of Sirens may vary across cultures, they all share the common theme of alluring and deceptive qualities. These mythical beings serve as cautionary reminders of the dangers of temptation and the importance of being wary when confronted with alluring promises.
Centaur
The majestic centaur, a half-human and half-horse hybrid, has been a prominent figure in ancient mythology. These mythical creatures are often depicted as noble and wise beings, embodying strength, agility, and an intimate connection with nature. They symbolize the duality of man and beast, uniting the human intellect with the untamed wildness of the animal kingdom. Centaurs are often portrayed as skilled archers, embodying both physical prowess and a deep understanding of the natural world. In ancient Greek mythology, centaurs were known for their wisdom and association with arts such as medicine and astrology. While their depictions may vary across cultures and time periods, the symbolism of the centaur continues to captivate our imaginations as a harmonious blend of humanity and nature, urging us to embrace the balance between our rational and instinctual selves.
The Majestic Centaur
The majestic centaur is a mythical creature that combines the body of a human with the lower body of a horse. Originating from Greek mythology, centaurs are often depicted as strong, agile beings known for their incredible speed and skill in archery. Centaurs symbolize the duality of man and nature, representing the harmony or conflict between our human intellect and our primal instincts. They embody the wild, untamed spirit of the wilderness, yet possess the intelligence and wisdom of human beings. The centaur’s human torso and equine lower body serve as a metaphor for the balance between our physical and spiritual nature. In some stories, centaurs are portrayed as noble beings, wise teachers, or courageous warriors. However, in other myths, they are often depicted as savage and wild, indulging in excessive indulgence and violence. Regardless of their portrayal, the centaur remains a powerful symbol of the intricate relationship between mankind and the natural world, serving as a reminder of our own inner conflicts and the constant struggle to find harmony within ourselves and our surroundings.
Symbolism of the Centaur
The symbolism of the centaur in mythology is rich and multi-faceted. With the upper body of a human and the lower body of a horse, the centaur represents the union of both intellect and instinct. This duality points to the centaur’s embodiment of the balance between civilization and wild nature, the rational and the primal. The human upper body signifies wisdom, knowledge, and the pursuit of intellectual pursuits, while the horse lower body symbolizes untamed strength, freedom, and the raw power of the natural world. The centaur’s hybrid form also represents the integration of opposites within ourselves, reminding us of the need to reconcile our own conflicting desires and impulses. Additionally, the centaur is often associated with the concept of mastery over the animalistic aspects of our nature, as well as the quest for self-discovery and self-control. In some mythologies, centaurs are depicted as wise teachers or healers, guiding others on their journey of self-realization. The symbolism of the centaur serves as a profound reminder of the complex and interconnected nature of human existence, urging us to find harmony between our intellect and our primal instincts. To learn more about the symbolism of snakes in mythology, you can read about it in my article on the symbolic meaning of snakes in mythology.
Centaur in Ancient Mythology
In ancient mythology, the centaur was a creature with the upper body of a human and the lower body of a horse. This fascinating hybrid being played a significant role in the mythology of ancient Greece, particularly in relation to their encounters with heroes and gods. Centaurs were often depicted as wild and savage creatures, known for their ferocity in battle and unruly behavior. However, there were exceptions, such as Chiron, a wise and gentle centaur who was known for his wisdom and skill in medicine and education. Despite their half-human, half-animal form, centaurs were often seen as symbols of duality, representing the conflicting aspects of human nature. They embodied both the noble qualities of humanity and the untamed instincts of the animal world. In ancient Greek mythology, centaurs were frequently depicted in various tales and were often associated with wine and revelry. Their representation in art and literature serves as a reminder of the complexity and multifaceted nature of human existence. The stories involving centaurs in ancient mythology provide insight into the human psyche, exploring themes of morality, self-control, and the eternal struggle between the divine and the animalistic within each individual. To understand the rich symbolism embedded within the ancient mythologies of centaurs is to unravel the depths of human nature and the intricacies of the human experience.
Mermaid

The enchanting mermaid, half-human and half-fish, has a prominent place in the folklore and mythology of various cultures around the world. These alluring aquatic beings have captured the imaginations of sailors, artists, and dreamers alike. With their mesmerizing beauty and melodious voices, mermaids are often associated with concepts of love, desire, and mystery. In some tales, they are seen as benevolent creatures, guiding ships to safety or granting wishes to those who encounter them. However, in other legends, they are depicted as luring sailors to their demise with their seductive songs. From ancient Greek tales of sirens to the folklore of coastal communities, mermaids continue to be a source of fascination and symbolism, representing the depths of the ocean and the duality of human nature. Whether they are creatures of peril or protectors of the sea, mermaids evoke an irresistible sense of wonder and intrigue.
The Enchanting Mermaid
The enchanting mermaid, a half-human, half-fish creature, has long captured the imagination and curiosity of people around the world. Often depicted as beautiful and alluring, mermaids are known for their mystical beauty and seductive voices. Legends of mermaids exist in various cultures, from the sirens of Greek mythology to the Ningyo of Japanese folklore. These captivating beings are believed to reside in the depths of the oceans, beckoning sailors with their melodic songs and tempting them with the promise of love and adventure. With their mesmerizing appearance and mysterious allure, mermaids have become symbols of both danger and enchantment. They represent the balance between the human and aquatic worlds, embodying the duality of nature. Mermaids have also become popular figures in literature, art, and popular culture, further cementing their status as iconic mythical creatures. Their transformative tales of love, sacrifice, and the depths of the sea continue to fascinate and inspire, reminding us of the immense wonders that lie beneath the ocean’s surface.
Symbolism of the Mermaid
The symbolism of the mermaid holds a deep significance in folklore and mythology. As elusive and captivating creatures of the sea, mermaids symbolize duality and the balance between two worlds – the land and the ocean. They embody beauty, grace, and feminine allure, often depicted with long flowing hair, shimmering tails, and enchanting voices that can both seduce and enchant sailors. In many tales, mermaids represent the harmony between humans and nature, acting as intermediaries between the two realms. They are often associated with love, temptation, and the depths of the subconscious mind. The mermaid’s dual nature, half-human and half-fish, symbolizes the merging of opposites and the exploration of both the conscious and unconscious aspects of our existence. Just as the sea is both alluring and treacherous, mermaids represent the ever-changing and unpredictable nature of life. In some cultures, they are seen as protectors of sailors, offering guidance and protection on their journeys. The symbolism of the mermaid varies across different cultures, but their allure and mystique remain universal, captivating the imagination and reminding us of the depths and wonders that lie beneath the surface.
Mermaids in Various Cultures
Mermaids, fascinating aquatic creatures with the upper body of a human and the tail of a fish, have captured the imaginations of people across various cultures around the world. In Greek mythology, the sea nymphs known as Nereids were often depicted as mermaids, embodying beauty and alluring charm. In Scandinavian folklore, the mermaid-like beings known as “sirens” were believed to possess enchanting voices that could lure sailors to their doom. The Irish legends speak of “merrow,” mermaids who were both beautiful and elusive, living in the depths of the ocean. In the folklore of the Philippines, “Sirena” is a half-human, half-fish creature that possesses the ability to bring good fortune to fishermen. These examples highlight the widespread presence and enduring fascination with mermaids in different cultures. Whether viewed as benevolent creatures or beware their captivating presence, mermaids continue to play a significant role in folklore and remain a symbol of the mystical and untamed wonders of the sea.
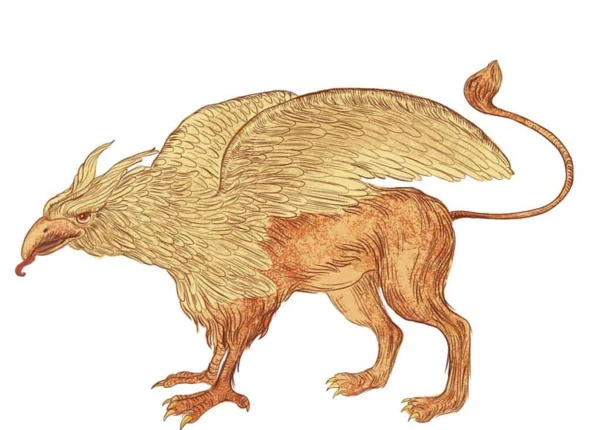
Griffin
The regal griffin, a creature of mythical proportions, is a captivating fusion of a lion and an eagle. This majestic beast is often associated with power, wisdom, and vigilance. With the body of a lion and the head, wings, and talons of an eagle, the griffin represents the harmonious balance between the land and the sky, embodying both terrestrial strength and aerial prowess. In ancient mythology, the griffin was believed to guard treasures and protect divine realms. Its vigilant nature and formidable presence made it a symbol of protection and guardianship. From ancient Mesopotamia to medieval Europe, the griffin’s presence can be found in various civilizations, engraved on sculptures, emblazoned on coats of arms, and woven into tales of heroism and adventure. This mythical creature continues to captivate our imagination with its majestic form and the symbolism it holds as a guardian of the sacred and a symbol of strength and nobility.
The Regal Griffin
The regal griffin stands as a majestic creature in the realm of mythology, combining the noble characteristics of both a lion and an eagle. This chimeric being is often depicted with the body of a lion, representing strength, courage, and sovereignty, and the head and wings of an eagle, symbolizing power, keen vision, and authority. The griffin’s appearance alone commands awe and respect, reflecting its significance as a symbol of grandeur and protection. In ancient Greek and Egyptian mythology, the griffin was regarded as a guardian figure, often associated with divine powers and the protection of treasures. Its presence was believed to ward off evil and bring good fortune. The griffin’s regal nature is further emphasized by its association with royalty and power, frequently seen as the emblem of noble families and a symbol of sovereignty. Through its mythical presence, the griffin embodies the harmonious fusion of majestic creatures, representing the union of earthly and heavenly realms. It continues to captivate our imagination as a symbol of strength, wisdom, and majesty.
Symbolism of the Griffin
The Griffin, a majestic creature with the head, wings, and talons of an eagle and the body of a lion, is steeped in symbolism across different mythologies. It represents a powerful combination of two mighty creatures, embodying the strength, courage, and nobility associated with both eagles and lions. The Griffin is often seen as a guardian or protector, revered for its ability to ward off evil and bring divine intervention. Its eagle-like qualities symbolize vision, wisdom, and spiritual insight, while the lion attributes represent courage, leadership, and sovereignty. As a result, the Griffin is often associated with royalty, serving as a symbol of power and authority. In medieval European folklore, Griffin imagery was prevalent in heraldry, adorning coats of arms and representing chivalry and nobility. The Griffin’s captivating symbolism extends beyond just physical prowess, encapsulating the fusion of wisdom, strength, and nobility to create a truly regal creature that continues to inspire awe and admiration.
Griffins in Mythology
In the vast realm of mythology, griffins stand as majestic and mythical creatures that have made their mark across various cultures. Depicted as creatures with the body of a lion and the head and wings of an eagle, griffins have symbolized a unique blend of power, strength, and wisdom. In Greek mythology, these magnificent creatures were believed to be guardians of treasures and protectors against evil. With their keen vision and powerful wings, griffins were often associated with the divine and considered to be the king of all creatures. Griffins also appeared in ancient Persian, Egyptian, and Scythian folklore, each culture offering their own interpretation and symbolism to these extraordinary beings. They were revered for their ability to soar through the skies and their role as protectors of valuable possessions. Soaring through the annals of mythology, griffins have left an indelible mark as symbols of power and nobility, embodying the union of strength and grace. Their presence in ancient tales and their representations in art and literature further solidify their status as enduring and revered creatures of myth and legend.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the mythical creatures discussed in this article hold a significant place in folklore and mythology, captivating our imaginations and instilling a sense of wonder. Each creature possesses its own unique symbolism, often reflecting various aspects of human nature and the world we inhabit. The unicorn, with its grace and purity, represents strength and miracles, offering a glimpse into the ethereal realm. Dragons, ancient and powerful, embody both fear and wisdom, symbolizing strength, protection, and transformation. The phoenix, with its ability to rise from the ashes, represents resilience, renewal, and the cycle of life. Sirens, mystical and alluring, serve as a cautionary reminder of the dangers of temptation and the power of their enchantment. Centaurs, half-human and half-horse, represent the duality of our nature and the blending of both physical and intellectual strengths. Mermaids, with their beauty and enchanting songs, embody the depths of emotion and the mysteries of the sea. Finally, the griffin, a majestic creature with the body of a lion and the head of an eagle, embodies nobility, courage, and the union of heaven and earth. Through exploring the symbolism and presence of these mythical creatures in various cultures, we gain a deeper understanding of our own human experiences and the universal themes that connect us all.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the origin of the unicorn myth?
The origin of the unicorn myth can be traced back to ancient civilizations, including Mesopotamia and ancient Greece. However, the unicorn as we know it today gained popularity during the medieval period in Europe.
Are unicorns real?
No, unicorns are not real creatures. They exist solely in mythology, folklore, and the imaginations of humans. Despite various legends and stories, there is no scientific evidence to support the existence of unicorns.
What is the symbolism behind the unicorn’s horn?
The unicorn’s horn, also known as an alicorn, has been attributed with various symbolic meanings. It is often associated with purity, healing, and protection against evil. In some cultures, it was believed that the horn possessed magical properties and could detect poison.
Do unicorns only appear in Western folklore?
No, unicorns are not limited to Western folklore. Similar mythical creatures have been found in the mythologies of other cultures, such as the qilin in Chinese mythology and the kirin in Japanese folklore.
What is the significance of the unicorn in heraldry?
In heraldry, the unicorn is a symbol of strength, courage, and purity. It is often depicted as a fierce creature, symbolizing the fighting spirit and noble qualities of its bearer.
Are there any famous literary works featuring unicorns?
Yes, unicorns have made appearances in various literary works. One notable example is “The Last Unicorn” by Peter S. Beagle, which follows the journey of a lone unicorn searching for her kind.
Do unicorns have any connections to astrology?
While unicorns are not directly associated with astrology, there is a constellation named Monoceros, which means “unicorn” in Latin. However, the constellation itself is not widely recognized or commonly used.
Are there any real animals that resemble unicorns?
While there are no real animals that precisely resemble unicorns, some animals have been mistakenly associated with them in folklore, such as the Indian rhinoceros, with its single horn.
Can unicorns fly?
In most folklore and mythologies, unicorns are not depicted as flying creatures. They are typically portrayed as graceful and agile beings that roam the earth.
What is the significance of the unicorn in modern culture?
The unicorn has experienced a resurgence in popular culture in recent years. It is often associated with magic, fantasy, and whimsy, and has become a popular motif in fashion, art, and various forms of media.
References
- Mythical creature
- Ten Mythical Creatures in Ancient Folklore from Around …
- Fantasy & Mythical Creatures Symbolism & Meaning
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What is the origin of the unicorn myth?
The origin of the unicorn myth can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and ancient Greece.
2. What does the unicorn symbolize in folklore?
The unicorn symbolizes purity, grace, and innocence in folklore.
3. Are there any real-life animals similar to the unicorn?
While there are no real-life animals with a single horn on their forehead like the unicorn, some species, such as the narwhal, have horn-like structures.
4. What are some cultural variations of the unicorn?
In Chinese culture, the Qilin is a mythical creature often associated with the unicorn. In South American folklore, the unicorn is known as the Camahueto.
5. What is the significance of dragons in mythology?
Dragons are often seen as powerful and wise creatures in mythology, representing both chaos and protection.
6. What do dragons symbolize in different cultures?
In Chinese culture, dragons symbolize good luck and are associated with the emperor. In Western cultures, dragons are often depicted as fierce and dangerous creatures.
7. Are there any notable stories involving dragons in different mythologies?
One famous story involving dragons is the legend of St. George and the Dragon, where St. George slays a dragon to save a princess.
8. What is the significance of the phoenix in folklore?
The phoenix is often associated with rebirth and immortality, representing the cycle of life, death, and resurrection.
9. How is the symbol of the phoenix used in various cultures?
In ancient Egypt, the phoenix represented the Sun God, Ra. In Greek mythology, the phoenix symbolized the power of transformation and regeneration.
10. Are there any other mythical creatures similar to sirens?
Similar to sirens, there are mythical creatures like the mermaid in various cultures, such as the selkie in Scottish folklore and the nereids in Greek mythology.