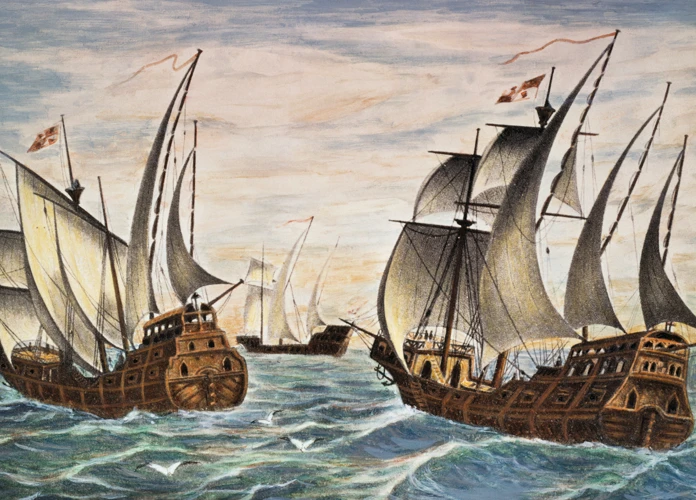
The Age of Exploration: Pioneers and Discoveries that Shaped the World
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
The Age of Exploration stands as a remarkable period in human history when intrepid voyagers set forth on perilous journeys to uncharted territories. Countless pioneers risked life and limb in search of new lands, riches, and the advancement of knowledge. With courage that defied the unknown, these explorers not only unveiled new lands but also revolutionized global trade and forever altered the course of human civilization. Join us as we embark on a captivating journey through history, uncovering the remarkable stories of these pioneering adventurers, and exploring the groundbreaking discoveries that transformed the world as we know it.
Contents
- Pioneers of the Age of Exploration
- Discoveries that Transformed the World
- Impact on Trade and Globalization
- Legacy and Influence
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Who financed Christopher Columbus’s voyage to the Americas?
- 2. How long did it take for Ferdinand Magellan’s expedition to circumnavigate the globe?
- 3. What was the main motivation behind Vasco da Gama’s journey to India?
- 4. Which new lands did Christopher Columbus discover in his voyages?
- 5. What were the Spice Islands and why were they significant?
- 6. Why was the Cape of Good Hope a significant discovery?
- 7. How did the Age of Exploration impact global trade?
- 8. What lasting influences did the Age of Exploration have on the world?
- 9. Who were some other notable explorers during the Age of Exploration?
- 10. How did the Age of Exploration contribute to our understanding of the world?
- References
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How did the Age of Exploration impact European nations?
- 2. Who financed the voyages of exploration?
- 3. What were the motivations for exploration during this time?
- 4. How did the discovery of the New World impact Native American populations?
- 5. What role did technological advancements play in the Age of Exploration?
- 6. How did the Age of Exploration contribute to the spread of global trade?
- 7. What impact did the discovery of the Spice Islands have on European economies?
- 8. How did the Age of Exploration lead to the rise of mercantilism?
- 9. What were the long-term consequences of the Age of Exploration?
- 10. How did the Age of Exploration pave the way for future scientific advancements?
- References
- Read More
Pioneers of the Age of Exploration
The pioneers of the Age of Exploration were intrepid individuals who ventured into the unknown, driven by a desire to expand the boundaries of human knowledge and achieve remarkable feats. Amongst these pioneers was Christopher Columbus, whose groundbreaking voyage to the Americas in 1492 opened up a new world of possibilities and reshaped our understanding of geography. Ferdinand Magellan, another renowned explorer, embarked on a daring expedition that resulted in the first circumnavigation of the globe, proving that the Earth was indeed round. Vasco da Gama, a Portuguese navigator, bravely sailed around the treacherous Cape of Good Hope, establishing a direct trade route to India. These pioneers defied the constraints of their time, facing unimaginable challenges, and their discoveries paved the way for future explorations that would shape the course of history.
1. Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was a visionary explorer who embarked on a historic voyage in 1492 that forever altered the course of human history. Born in Genoa, Italy, Columbus was driven by a relentless desire to find a new trade route to Asia. Armed with a bold belief that the Earth was round, he secured the support of Queen Isabella and King Ferdinand of Spain. Columbus set sail with three ships, the Santa Maria, the Pinta, and the Niña, and after a treacherous journey, he made landfall in the Bahamas, thus discovering the New World.
Columbus’ journey across the Atlantic Ocean not only brought him to the Americas but also ignited a new wave of exploration and colonization. His groundbreaking voyage paved the way for further European expeditions to the New World, leading to the colonization and eventual founding of numerous American colonies that would shape the future of the Americas.
Despite his achievements, Christopher Columbus’s legacy is not without controversy. While celebrated for his exploration, his arrival also marked a devastating period for indigenous populations. As we examine the impact of his voyages, it’s crucial to acknowledge the complex and often tragic consequences that unfolded as a result.
Today, Christopher Columbus remains an integral figure in the Age of Exploration. His courageous journey opened up a new era of discovery, forever changing the global map and setting the stage for the interconnected world we live in today. For more details on the historical context and significance of discoveries, you can read about unraveling zodiac symbol meanings.
2. Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer, is renowned for leading the first circumnavigation of the globe. In 1519, Magellan embarked on an ambitious expedition with a fleet of five ships, aiming to find a western route to the “Spice Islands” in the East Indies. Despite facing numerous challenges and setbacks, including mutinies and hostile encounters with indigenous peoples, Magellan’s unwavering determination propelled him forward. He discovered the strait that now bears his name, allowing his fleet to reach the vast Pacific Ocean. As they sailed westward, enduring hardships such as scurvy and treacherous weather conditions, Magellan’s crew became the first to witness the enormity of the Pacific. The expedition faced its greatest test as they reached the Philippines, where Magellan tragically lost his life in a skirmish with local tribes. However, one of his ships, the Victoria, successfully completed the circumnavigation under the command of Juan Sebastián Elcano. This historic journey not only proved that the Earth was round but also solidified the concept of a global maritime trade network. Magellan’s courageous voyages paved the way for future explorations and forever changed our understanding of the world.
3. Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, a remarkable Portuguese explorer, played a pivotal role in the Age of Exploration. In the late 15th century, he embarked on a treacherous journey with the goal of finding a direct sea route from Europe to India. Da Gama’s voyage led him to navigate around the treacherous Cape of Good Hope, a feat that had never been accomplished before. By successfully reaching the port of Calicut in India, he established a lucrative trade route between Europe and the East. The discovery of this new route brought immense wealth to Portugal and opened up opportunities for global trade on an unprecedented scale. Da Gama’s courage and determination not only cemented his place in history but also laid the foundation for future explorers to follow in his footsteps. To commemorate his accomplishments, a statue of Vasco da Gama stands in Lisbon, a testament to his enduring legacy and the impact he had on shaping the world.
Discoveries that Transformed the World
The discoveries made during the Age of Exploration were nothing short of revolutionary, shaping the world in profound ways. The first and undoubtedly one of the most impactful discoveries was that of The New World. Christopher Columbus’s journey to the Americas opened up a vast expanse of uncharted lands and set in motion centuries of exploration and colonization. Equally significant were the discoveries of The Spice Islands, which sparked a fierce competition among European powers to control the lucrative spice trade and led to the establishment of global trading networks. Additionally, the exploration of The Cape of Good Hope by Portuguese navigators like Bartolomeu Dias and Vasco da Gama proved that a sea route to India was feasible, revolutionizing global trade and forever altering the balance of power. These extraordinary discoveries not only enriched the world economically but also led to cultural exchange, scientific advancements, and the integration of diverse societies.
1. The New World
The discovery of the New World was an extraordinary event that reshaped the course of human history. This momentous achievement is often attributed to Christopher Columbus, whose voyage in 1492 unveiled a land previously unknown to Europeans. The New World, famously referred to as the Americas, presented a wealth of new opportunities and resources for exploration, colonization, and trade. It ignited a fervor for exploration and colonization, with European powers vying for control over these untapped lands. The introduction of new plants, animals, and resources from the New World revolutionized economies, leading to the Columbian Exchange and ultimately transforming the global balance of power. The discovery of the New World also had profound cultural and social impacts. It spurred the blending of cultures, languages, and ideas, forever altering the fabric of societies. This new chapter in human history brought both prosperity and devastation, as indigenous populations faced colonization, exploitation, and conflict. The exploration and colonization of the New World remains an essential milestone in the Age of Exploration, leaving an indelible mark on the course of human civilization.
2. The Spice Islands
The Spice Islands, also known as the Moluccas, were a group of islands located in Indonesia that played a pivotal role in shaping the course of world history. These islands were renowned for producing highly prized spices such as cloves, nutmeg, and mace, which were in high demand throughout Europe. The allure of these exotic spices sparked a fervent desire among European explorers to find a direct trade route to the source. In the early 16th century, Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan set sail on a daring expedition in search of the Spice Islands. His voyage, which ultimately led to the first circumnavigation of the globe, solidified the importance of these islands as a hub of global trade. The Spice Islands became a coveted prize among European powers, leading to fierce competition and conflicts that shaped the geopolitics of the era. The spice trade transformed European economies, spurred the growth of capitalism, and fueled the Age of Exploration. To this day, the Spice Islands remain a testament to the impact that a humble ingredient can have on the course of human history.
3. The Cape of Good Hope
Located on the southern tip of Africa, the Cape of Good Hope played a pivotal role in the Age of Exploration. This treacherous cape, discovered by the Portuguese explorer Bartolomeu Dias in 1488, provided a crucial passage for sailors navigating between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Sailing around the Cape of Good Hope allowed explorers to access lucrative trade routes to Asia, bringing valuable goods such as spices, silk, and porcelain to Europe. The cape’s significance extended beyond trade, as it also served as a strategic point for the establishment of colonies and control over maritime routes. Its discovery and subsequent use as a navigational landmark opened up new possibilities for exploration and trade, shaping the development of global commerce and establishing European dominance in the Indian Ocean. Today, the Cape of Good Hope is a popular tourist destination, allowing visitors to marvel at the stunning landscapes and immerse themselves in the rich history of this legendary landmark.
Impact on Trade and Globalization
The Age of Exploration had a profound impact on trade and globalization, forever altering the economic landscape of the world. The discovery of new trade routes, such as the sea route to India by Vasco da Gama, revolutionized the spice trade and opened up lucrative opportunities for merchants and traders. The exploration of the Americas by Christopher Columbus also led to the establishment of vast colonial empires, enriching European nations through the exploitation of resources and the establishment of trade networks. The influx of newly discovered goods, such as exotic spices, precious metals, and unique flora and fauna, sparked a global demand that fueled the growth of international trade. The exchange of knowledge, ideas, and cultural practices between different regions facilitated by these explorations contributed to the process of globalization. The exploration and colonization of new territories led to the integration of diverse societies, languages, and customs into the global network, shaping the world we know today. This period of discovery and expansion laid the foundation for a globalized world, connecting distant lands and peoples in ways that were previously unimaginable. The impact of the Age of Exploration on trade and globalization continues to reverberate throughout history, leaving an indelible mark on the development of human civilization.
Legacy and Influence

The legacy and influence of the Age of Exploration can be felt in numerous aspects of our modern world. The voyages and discoveries made during this time period revolutionized the fields of geography, cartography, and navigation. Explorers like Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, and Vasco da Gama shattered the misconceptions and limitations of the known world, expanding our understanding of the Earth’s geography and prompting further exploration. The explorations also resulted in the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture between different regions, leading to the phenomenon of globalization. The spice trade, for instance, was greatly influenced by these explorations, as new routes were established to access valuable spices from the East. The explorers’ interactions with indigenous populations also left a lasting impact on the world, with both positive and negative consequences. The encounters and conquests laid the groundwork for the establishment of colonies and the spread of European influence around the world. Additionally, the discoveries made during the Age of Exploration fueled a spirit of scientific inquiry and curiosity, inspiring future generations of explorers, scientists, and innovators. The navigational techniques and instruments developed during this time period set the stage for further advancements in maritime technology and exploration in centuries to come. The legacy of these pioneering individuals continues to shape our world today, reminding us of the power of human curiosity, courage, and the pursuit of knowledge.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the Age of Exploration stands as a testament to human curiosity, bravery, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. The pioneers of this era, including Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, and Vasco da Gama, embarked on perilous journeys that would forever reshape our understanding of the world. Through their voyages, new lands were discovered, trade routes were established, and civilizations collided. The discoveries made during this time revolutionized global trade, sparked the age of colonization, and laid the foundation for the interconnected world we live in today. The legacy of these pioneering explorers lives on through the cultural exchange, scientific advancements, and global perspective that emerged as a result of their endeavors. The Age of Exploration serves as a reminder that there is always more to be discovered and that the human spirit of exploration and discovery knows no bounds. As we look back on this transformative period in history, we are reminded of the indomitable human spirit and the power of exploration to shape the world.
References:
– “Unraveling Zodiac Symbol Meanings.” [Link](/unraveling-zodiac-symbol-meanings/)
– “Fascinating Legends in Japanese Mythology.” [Link](/fascinating-legends-japanese-mythology/)
– “Snake Symbolism Unraveled: Ophiuchus Myth.” [Link](/snake-symbolism-unraveled-ophiuchus-myth/)
Frequently Asked Questions

1. Who financed Christopher Columbus’s voyage to the Americas?
Christopher Columbus’s voyage to the Americas was financed by Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, rulers of what is now modern-day Spain.
Ferdinand Magellan’s historic expedition took approximately three years, from 1519 to 1522, to complete the first circumnavigation of the globe.
3. What was the main motivation behind Vasco da Gama’s journey to India?
Vasco da Gama’s main motivation for his journey to India was to establish a direct sea route to the valuable spice trade, bypassing the overland routes controlled by Arab middlemen.
4. Which new lands did Christopher Columbus discover in his voyages?
Christopher Columbus discovered several new lands during his voyages, including the Caribbean islands, Central and South America. He mistakenly believed he had reached the East Indies.
5. What were the Spice Islands and why were they significant?
The Spice Islands, also known as the Moluccas, were a group of islands in Southeast Asia known for their abundance of valuable spices such as cloves, nutmeg, and mace. These spices were highly sought-after and played a crucial role in shaping the global economy and driving exploration during the Age of Exploration.
6. Why was the Cape of Good Hope a significant discovery?
The Cape of Good Hope, located at the southern tip of Africa, was a significant discovery as it provided European explorers with a sea route to Asia. Prior to this discovery, sailors had to navigate perilous overland routes to access the lucrative trade markets of the East.
7. How did the Age of Exploration impact global trade?
The Age of Exploration had a profound impact on global trade by expanding trade routes and connecting distant regions of the world. It facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas, laying the foundation for the globalized world we live in today.
8. What lasting influences did the Age of Exploration have on the world?
The Age of Exploration brought about lasting influences such as the establishment of colonial empires, the spread of Christianity, the exchange of plants and animals between continents (known as the Columbian Exchange), advancements in navigation and cartography, and the emergence of a global economy.
9. Who were some other notable explorers during the Age of Exploration?
Alongside Christopher Columbus, Ferdinand Magellan, and Vasco da Gama, other notable explorers of the Age of Exploration include Amerigo Vespucci, Henry Hudson, James Cook, and Sir Francis Drake, among many others.
10. How did the Age of Exploration contribute to our understanding of the world?
The Age of Exploration played a vital role in expanding our understanding of the world. It challenged existing geographical knowledge, disproving the notion that the Earth was flat, and contributed to the development of more accurate maps. Additionally, it expanded knowledge in various scientific disciplines, including astronomy, botany, and anthropology, through the exploration and documentation of new lands and cultures.
References
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How did the Age of Exploration impact European nations?
The Age of Exploration had a profound impact on European nations by expanding their territories, increasing their wealth and power, and fostering technological advancements.
2. Who financed the voyages of exploration?
The voyages of exploration were typically financed by wealthy individuals or monarchs who saw the potential for economic gain and sought to expand their influence.
3. What were the motivations for exploration during this time?
The motivations for exploration during this time were primarily driven by the desire to find new trade routes, acquire valuable resources, spread Christianity, and gain prestige and glory.
4. How did the discovery of the New World impact Native American populations?
The discovery of the New World had a devastating impact on Native American populations through colonization, slavery, diseases, and cultural assimilation.
5. What role did technological advancements play in the Age of Exploration?
Technological advancements, such as improved ship design, navigational instruments like the astrolabe and compass, and the development of cartography, greatly facilitated the voyages of exploration.
6. How did the Age of Exploration contribute to the spread of global trade?
The Age of Exploration played a significant role in the expansion of global trade by establishing new trade routes, connecting previously isolated regions, and introducing new goods and resources to different parts of the world.
7. What impact did the discovery of the Spice Islands have on European economies?
The discovery of the Spice Islands, also known as the Moluccas, had a profound impact on European economies as the highly sought-after spices brought immense wealth and sparked the development of global trade networks.
8. How did the Age of Exploration lead to the rise of mercantilism?
The Age of Exploration contributed to the rise of mercantilism, an economic theory that advocated for a nation’s self-sufficiency and accumulation of wealth through trade and colonization, as nations sought to control valuable resources and establish monopolies.
9. What were the long-term consequences of the Age of Exploration?
The long-term consequences of the Age of Exploration include the establishment of colonial empires, the integration of different cultures and societies, the exchange of ideas, the reshaping of global power dynamics, and the beginning of modern globalization.
10. How did the Age of Exploration pave the way for future scientific advancements?
The Age of Exploration paved the way for future scientific advancements by promoting the study of geography, astronomy, and cartography, encouraging scientific inquiry, and fostering the exchange of knowledge and ideas among different cultures.
References
- 2 Age of Exploration | History Hub
- Age of Exploration and Discovery – Renaissance for Kids
- The Age of Exploration






